Troubleshooting Wi Fi Dead Zones Tips to Extend Your Wireless Network Coverage

MakeUseOf
We take Wi-Fi for granted, but it's not magic---it's made up of radio waves which solid objects can block and interfere with. Fortunately, there are ways to locate and eradicate dead zones so you can enjoy the internet anywhere in the home.
Let's explore why Wi-Fi dead zones exist, and how to solve them.
What Is a Wi-Fi Dead Zone?
A dead zone is simply an area within your house, apartment, office, or any other area that's supposed to be covered by Wi-Fi. When you try to connect, however, your device registers no signal.
If you take a device into a dead zone, the Wi-Fi will stop working and you won't receive a signal. For example, if you walk into a room with a phone or tablet, and that room is in a dead zone, you'll stop getting a Wi-Fi signal.
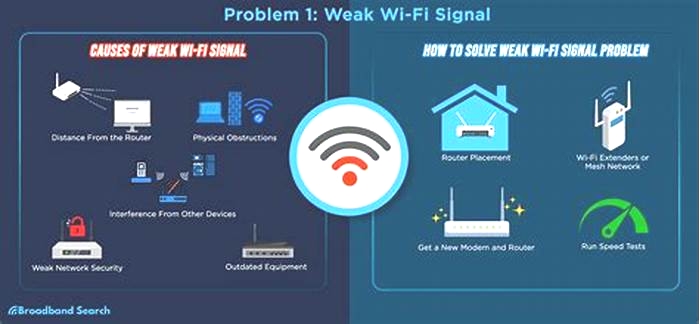
What Causes Wi-Fi Dead Zones in a House?
Anything that interferes with Wi-Fi radio waves produces a dead zone. If you have a large house or office and have your wireless router in one corner of the building, there may be a dead zone in the opposite corner of the building where the Wi-Fi signal can't reach.
Most houses were built before Wi-Fi was developed, so the floorplan and building materials may interfere with Wi-Fi. Old houses may have thick plaster walls that contain chicken wire for support, and this metal wiring can block Wi-Fi signals. Large metal objects like filing cabinets or metal walls may also block a Wi-Fi connection.
Other devices can also interfere with your connection. Old cordless phones create Wi-Fi dead spots while in use, and a microwave oven blocks Wi-Fi signals while running. Baby monitors, wireless security systems, and wireless sound systems have also been known to cause Wi-Fi issues.
If you live in an area dense with other wireless broadcasts, your Wi-Fi coverage may also be hurt by interference. For example, if you lived an apartment block where every unit has its own wireless router, their signals may "fight."
Similarly, if your nearby neighbors have their Wi-Fi networks configured on the same wireless channel as yours, this may result in interference, reducing your network's signal strength. This can result in dead zones around your home.
How to Detect Wireless Dead Zones
You don't need special software to identify dead zones. Just pick up your smartphone or another wireless device, connect to your wireless network, and walk around.
Pay attention to the Wi-Fi signal indicator on your smartphone. If signal strength drops to zero, you've found a dead zone.
Even if the Wi-Fi signal only drops to a very low level, be sure to take note of it. Unreliable signal strengths may result in slower speeds or prevent devices from connecting altogether.
Remember that the Wi-Fi indicator doesn't update immediately, so don't sprint while holding your phone. Walk slowly and pause in areas where you might conceivably use Wi-Fi.
Of course, you can also use software to help detect wireless dead zones. On Android, the free Wifi Analyzer app will show you more detailed information about the strength of your Wi-Fi signal.
Open the app, select the Signal meter screen, and pick your Wi-Fi network. Walk around with the app open and you'll see the signal strength change as you move from location to location.
Apple doesn't allow third-party apps to access this information on iOS, so iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch users can't use an app for more detailed information---they'll have to pay attention to their device's standard Wi-Fi indicator.
If you have a Windows or macOS laptop, you could also use inSSIDer to measure your Wi-Fi signal strength. Be careful while walking around with your laptop and staring at its screen the whole time, however.
Download:Wifi Analyzer for Android (Free)
Download: inSSIDer for PC | macOS (Free)
How to Fix Wireless Dead Zones in the Home
Now that you've figured out exactly where your wireless dead zones are, you'll probably want to eliminate them. Here are some tips for patching up your Wi-Fi coverage.
Reposition Your Router to a Better Place
If your router is in one corner of your house, apartment, or office, there may be a dead zone in the opposite corner of your building. Try moving the router to a more central location in the middle of your house, apartment, or office.
Adjust or Replace Your Router's Antenna
Ensure your wireless router's antenna is up and pointing vertically. If it's pointing horizontally, you won't get the same amount of coverage. If your antenna is already at the perfect angle, try attaching a more powerful antenna for a wider broadcast range.
Identify and Reposition Obstructions Between You and the Router
If your Wi-Fi router is sitting next to a metal filing cabinet, that's going to reduce your signal strength. As such, try rearranging your place for ideal signal strength.
If there's a microwave oven, aquarium, or anything else that seems to be obstructing the signal from your router and producing a dead zone, move the obstruction (or your router) and see if that eliminates the dead zone.
Switch to the Least-Congested Wireless Channel
Use the tools we covered above to identify the least congested wireless channel for your Wi-Fi network. Once you find it, change your router's channel to it to reduce interference from other wireless networks.
Set Up a Wireless Repeater
If none of the above tips help,you could set up a wireless repeater to extend your coverage over a larger area. This may be essential in large houses or offices.
You can even turn unused routers into a wireless repeater, which is one of many ways to reuse an old router.
Use an Ethernet Connection
You could also get online using Ethernet cables. If your computer and router are close enough, connect the two using Ethernet and never worry about Wi-Fi signals dropping ever again.
Use a Pair of Powerline Adapters
If you're not so keen on seeing stray cables in the corridor, you can use powerline adapters instead. Plug one into the room with a dead zone, and the other into the room where the router is.
We talked more about what powerline adapters are previously, so be sure to give it a read if you're interested.
Pushing Your Wi-Fi Strength Further
Wi-Fi dead zones appear due to lots of different reasons. This includes router positioning, your neighbors, what your building's walls are made out of, the size of your coverage area, the types of electronic devices you have, and your furniture. There is much that can cause problems, but trial and error can help you pin down the culprit.
If you want to make your router's signal stronger, be sure you know how to boost your Wi-Fi signal and extend its range.
How to Get The Best WiFi Coverage
Analyze Your WiFi Coverage
The most important part of any endeavor is information. Before we start a long trip, we need to plan out the roads to use, where the rest stops will be, and places to sleep along the way.
Planning how to get the best WiFi coverage is a similar process. We need to understand just where our current WiFi network reaches, how strong it is in different areas, and where the weak points are. To do that, we need to use a WiFi analyzer. A WiFi analyzer works by taking a poll of each of the WiFi networks it can reach.
By transmitting data across the network, it measures how fast the network is, and checks the signal strength of the WiFi radio waves. A good WiFi analyzer does more than just check speed. It checks multiple networks, finds the frequency type of the WiFi radio signal, the strength of the signal, signal to noise ratio, and a host of other statistics.
Dont let the word statistics scare you a good WiFi analyzer can display that information in an easy to understand table format, or if its really good by showing off the information on a map.
This is why NetSpot works so well. Its a WiFi analyzer that works with Windows, Mac OS X, and Android devices. NetSpot provides incredible information gathering tools with a simple interface that anyone can understand. For registered users, NetSpot can use the information to build heat maps.
How To Create Mesh Network With Two Routers
Introduction
Welcome to the world of mesh networks, where reliable, seamless internet connectivity is within your reach. In todays digital age, having a stable and robust internet connection is essential for both work and leisure activities. However, certain areas of your home or office may experience weak Wi-Fi signals or dead zones, causing frustration and hindered productivity.
A mesh network is a solution to this problem, providing a network infrastructure that extends the coverage and improves the reliability of your wireless connection. With a mesh network, you can create a network that blankets your entire space, eliminating dead zones and ensuring a consistent and strong Wi-Fi signal throughout.
In this article, we will walk you through the process of creating a mesh network using two routers. This setup will help you overcome Wi-Fi limitations and provide you with a seamless internet experience. Whether you want to optimize the internet connection in your home, office, or any other space, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to set up your own mesh network.
Before we delve into the technical steps, lets explore the benefits of using a mesh network and discuss the requirements for creating one with just two routers.
What is a Mesh Network?
A mesh network is a type of wireless network infrastructure that consists of multiple interconnected devices, known as nodes or access points, that work together to provide seamless coverage and reliable internet connectivity. Unlike traditional Wi-Fi setups where a single router is responsible for transmitting signals, a mesh network distributes the load across multiple devices, resulting in improved performance and coverage.
In a mesh network, each node communicates with other nodes within the network, creating a self-healing and self-optimizing network. This means that if one node fails or encounters an issue, the other nodes automatically reroute the data to ensure uninterrupted connectivity. This dynamic routing capability is one of the key advantages of a mesh network.
Mesh networks are highly flexible and scalable, making them suitable for a wide range of environments, from small apartments to large office spaces. Additionally, mesh networks can support a high number of devices simultaneously, making them ideal for homes or workplaces with numerous connected devices.
One of the standout features of a mesh network is the ability to extend the Wi-Fi coverage area without sacrificing performance. By strategically placing nodes throughout your space, the network eliminates dead zones and ensures a strong and consistent signal strength in every corner.
Mesh networks are also known for their easy setup and management. Many modern routers and mesh network systems come with user-friendly mobile apps that guide you through the installation process and offer convenient management features. With just a few steps, you can have your mesh network up and running, providing seamless internet connectivity to all your devices.
In the next section, we will explore the various benefits of using a mesh network in more detail.
Benefits of Using a Mesh Network
Mesh networks offer several advantages over traditional Wi-Fi setups. Lets explore some of the key benefits:
- Extended Coverage Area: One of the primary advantages of a mesh network is the ability to extend the Wi-Fi coverage area. By strategically placing multiple nodes throughout your space, the network ensures a strong and consistent signal in every room, eliminating dead zones.
- Improved Performance: With a mesh network, the load is distributed among multiple nodes, resulting in improved performance. This means that even if you have numerous devices connected to the network, youll experience minimal lag and faster internet speeds.
- Seamless Roaming: Mesh networks offer seamless roaming, allowing your device to effortlessly switch between nodes as you move around your space. This means you wont experience any interruptions or drops in the Wi-Fi signal when transitioning from one area to another.
- Self-Healing Network: In a mesh network, if one node fails or encounters an issue, the network automatically reroutes the data through alternative paths. This self-healing capability ensures that your internet connection remains uninterrupted even if theres a problem with one of the nodes.
- Easy Setup and Management: Setting up a mesh network is typically straightforward, with many systems providing user-friendly mobile apps that guide you through the process. These apps also offer convenient management features, allowing you to monitor and control your network settings with ease.
- Scalability: Mesh networks are highly scalable, meaning you can easily expand your network by adding additional nodes as needed. Whether you want to cover more rooms, floors, or even an outdoor area, you can adapt your mesh network to meet your specific requirements.
- Enhanced Security: Many mesh networks come equipped with advanced security features, such as encryption and firewall protection. These built-in security measures help safeguard your network and protect your data from unauthorized access.
By leveraging the benefits of a mesh network, you can create a reliable, high-performing wireless network that caters to the demands of your home, office, or any other space.
Now that we understand the advantages of using a mesh network, lets move on to the requirements for creating a mesh network with just two routers.
Requirements for Creating a Mesh Network with Two Routers
Before you begin setting up a mesh network with two routers, its important to ensure that you have the necessary requirements in place. Heres what youll need:
- Two Compatible Routers: Select two routers that are capable of creating a mesh network. These routers should support mesh networking functionality and have the necessary features to communicate with each other.
- Strong Internet Connection: A stable and reliable internet connection is essential for creating and using a mesh network. Make sure that your primary router is connected to a reliable broadband internet source.
- Ethernet Cables: Youll need Ethernet cables to connect your routers. Ensure that you have long enough cables to connect the primary router to the modem and to connect the two routers together.
- Power Outlets: Ensure that you have adequate power outlets available near the locations where you plan to install the routers. Each router will require its own power source.
- Device with Web Browser: To configure the routers, youll need a device (such as a laptop or smartphone) with a web browser. This will allow you to access the routers web-based setup interface.
- Patience and Persistence: Setting up a mesh network with two routers may require some troubleshooting and configuration adjustments. Patience and persistence are key, especially if you encounter any issues along the way.
By ensuring that you have these requirements in place, youll be well-prepared to proceed with the setup process. In the next section, well guide you through the steps of choosing the right routers for your mesh network.
Step 1: Choosing the Right Routers
Choosing the right routers is crucial for creating a successful mesh network. Here are some factors to consider when selecting your routers:
- Mesh Networking Compatibility: Ensure that the routers you choose are specifically designed for mesh networking. These routers are equipped with the necessary features to seamlessly communicate with each other and create a mesh network.
- Brand and Model: Opt for routers from reputable brands that have a strong track record in delivering reliable networking solutions. Additionally, check for models that have positive reviews and ratings, indicating their performance and reliability.
- Specs and Features: Evaluate the specifications and features of the routers. Look for routers that support the latest Wi-Fi standards (such as 802.11ac or 802.11ax), have ample coverage range, and offer sufficient processing power to handle your network demands.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the routers. Look for routers that allow you to add additional nodes or expand the network if needed. This flexibility is important if you plan to extend your mesh network in the future.
- User-Friendly Setup: Check if the routers offer a user-friendly setup process. Some routers come with mobile apps that guide you through the installation and configuration steps, making the setup process easier and more accessible for beginners.
- Budget: Set a budget for your mesh networking project and choose routers that align with your financial constraints. Keep in mind that while quality routers may come with a higher price tag, they offer better performance and reliability, ensuring a smoother network experience.
By considering these factors, you can narrow down your options and choose the routers that best meet your needs. Its recommended to do thorough research, read customer reviews, and compare different models before making a final decision. The right routers will greatly contribute to the overall performance and stability of your mesh network.
Now that you have an understanding of the factors to consider when selecting routers, lets move on to configuring the primary router in the next section.
Step 2: Configuring the Primary Router
Once you have chosen the right routers for your mesh network, the next step is to configure the primary router. Follow these steps to set up the primary router:
- Connect the router to your modem: Use an Ethernet cable to connect the WAN (Wide Area Network) port on the primary router to the Ethernet port on your modem. This will establish the internet connection for your network.
- Power on the router: Plug the primary router into a power outlet and turn it on. Wait for the router to boot up and establish a connection with your modem.
- Access the routers web-based setup interface: Open a web browser on a device that is connected to the same network and enter the default IP address of the router in the browsers address bar. You can find the default IP address in the routers documentation or on the manufacturers website.
- Log in to the router: Enter the routers default username and password, which can also be found in the documentation. If you have changed the login credentials previously, use the updated information.
- Configure basic settings: Once logged in, you will have access to the routers web-based interface. Here, you can configure basic settings such as the network name (SSID) and password. Set these according to your preferences and ensure that they are secure.
- Enable mesh networking functionality: Look for the mesh networking or mesh mode setting in the routers interface. Enable this setting to allow the router to function as the primary node in the mesh network.
- Save and apply the settings: After configuring the necessary settings, save and apply the changes. The router will likely reboot to apply the new settings.
Once you have completed these steps, the primary router is configured and ready to establish the mesh network with the secondary router. In the next section, we will guide you through connecting the secondary router to the primary router.
Step 3: Connecting the Secondary Router to the Primary Router
Now that you have configured the primary router, its time to connect the secondary router to the primary router. Follow these steps to establish the connection:
- Place the secondary router: Determine the optimal location for the secondary router. It should be positioned within range of the primary router and in a location that helps extend the Wi-Fi coverage to the desired area.
- Connect the secondary router: Use an Ethernet cable to connect one of the LAN (Local Area Network) ports on the primary router to the WAN port on the secondary router. This will establish a wired connection between the two routers.
- Power on the secondary router: Plug the secondary router into a power outlet and turn it on. Wait for the router to boot up and establish a connection with the primary router.
- Access the secondary routers web interface: Open a web browser on a device connected to the primary routers network and enter the secondary routers IP address in the browsers address bar. You can find the IP address in the secondary routers documentation or on the manufacturers website.
- Log in to the secondary router: Enter the login credentials for the secondary router. If you havent made any changes, you can often find the default username and password in the documentation.
- Configure the secondary router: In the secondary routers web interface, navigate to the network settings and configure the necessary parameters. Ensure that the network name (SSID) and password match those of the primary router to create a seamless mesh network.
- Disable DHCP on the secondary router: In the network settings, disable the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server on the secondary router. This will prevent any conflicts between the two routers and ensure a smooth operation of the mesh network.
- Save and apply the settings: After configuring the secondary router, save and apply the changes. The router may reboot to implement the new settings.
Once these steps are completed, the secondary router is successfully connected to the primary router, establishing a mesh network. In the next section, we will guide you through the process of configuring the secondary router to work seamlessly within the mesh network.
Step 4: Configuring the Secondary Router
After successfully connecting the secondary router to the primary router, the next step is to configure the secondary router to work seamlessly within the mesh network. Follow these steps to configure the secondary router:
- Access the secondary routers web interface: Open a web browser on a device connected to the secondary routers network and enter the routers IP address in the browsers address bar. The IP address can be found in the routers documentation or on the manufacturers website.
- Log in to the secondary router: Enter the login credentials for the secondary router. If you havent made any changes, you can often find the default username and password in the documentation.
- Configure the wireless settings: In the secondary routers web interface, navigate to the wireless settings. Here, you need to ensure that the network name (SSID) and password match those of the primary router. This will ensure that all devices connected to the mesh network can seamlessly roam between the two routers.
- Disable DHCP on the secondary router: Still in the secondary routers web interface, locate the DHCP settings and disable the DHCP server. This prevents any conflicts with the primary router and ensures that IP addresses are properly assigned within the network.
- Configure any additional settings: Depending on the specific features and options available in your secondary routers web interface, you may want to configure additional settings, such as port forwarding, parental controls, or guest network setup. Set these according to your preferences and needs.
- Save and apply the settings: After configuring the secondary router, save and apply the changes. The router may reboot to implement the new settings.
Once these configuration steps are completed, the secondary router is now configured to function effectively within the mesh network. It will work in conjunction with the primary router to extend the coverage area and provide seamless connectivity throughout your space.
Now that you have both routers properly configured and connected, its time to test and ensure that the mesh network is functioning as desired. In the next section, we will guide you through the process of testing the mesh network.
Step 5: Testing the Mesh Network
After setting up and configuring your mesh network with two routers, its important to test the network to ensure that it is functioning as expected. Here are some steps you can take to test and evaluate the performance of your mesh network:
- Check Wi-Fi signal strength: Move around your space and check the Wi-Fi signal strength in different areas. Ensure that the signal remains strong and consistent, without any sudden drops or weak spots.
- Test internet speed: Use an internet speed testing tool to measure the download and upload speeds of your network. Compare the results to the expected speeds provided by your internet service provider (ISP).
- Connect multiple devices: Connect multiple devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, to the mesh network simultaneously. Ensure that all devices are able to connect without any issues and experience a stable internet connection.
- Roaming test: Move between different areas within your space while connected to the mesh network. Monitor how quickly and seamlessly your devices switch between the primary and secondary routers without any interruptions or dropouts.
- Streaming and gaming: Test streaming services and online gaming on devices connected to the mesh network. Evaluate the performance and stability of these activities to ensure that they are smooth and lag-free.
- Identify dead zones: Walk around your space and identify any areas where the signal strength is weak or non-existent. These dead zones may indicate areas that are not adequately covered by the mesh network, and you may need to reposition or add additional nodes to improve coverage.
By conducting these tests, you can assess the performance and coverage of your mesh network. If any issues or areas of improvement are identified during testing, you can take steps to address them, such as adjusting router positions, adding more nodes, or fine-tuning network settings.
With the mesh network successfully tested and optimized, you can now enjoy the benefits of a seamless and reliable internet connection throughout your home or office.
Congratulations! You have successfully created a mesh network with two routers. Enjoy the expanded coverage, improved performance, and hassle-free connectivity that your mesh network provides.
Conclusion
Creating a mesh network with two routers is a fantastic way to extend the coverage and enhance the performance of your Wi-Fi network. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can overcome the limitations of traditional routers and eliminate Wi-Fi dead zones in your home or office.
A mesh network offers a range of benefits, including extended coverage, improved performance, seamless roaming, self-healing capabilities, and easy setup and management. With the right routers and proper configuration, you can create a reliable and robust mesh network that caters to your specific needs.
Remember to choose routers that are compatible with mesh networking and offer the necessary features to create a seamless network. Properly configuring the primary and secondary routers, ensuring consistent wireless settings, and disabling DHCP on the secondary router are crucial steps for achieving optimal performance.
Testing the mesh network is an essential step to ensure its effectiveness. Check Wi-Fi signal strength, test internet speed, connect multiple devices, evaluate roaming capabilities, and identify any dead zones that may require adjustments or additional nodes.
By following these steps and taking the time to properly set up and test your mesh network, you can enjoy a reliable, high-performing, and seamless internet experience throughout your space.
Now that youre armed with the knowledge to create a mesh network with two routers, go ahead and transform your Wi-Fi experience. Embrace the power of a mesh network and enjoy enhanced connectivity in every corner of your home or office.