The Complete Tutorial on Using AutoCAD for Design Projects width

How to Learn AutoCAD: Complete free guide
AutoCAD, developed by Autodesk, is a powerful computer-aided design (CAD) software used extensively in various industries such as architecture, engineering, and design. Its versatility and widespread adoption make it an essential skill for professionals in these fields. In this article, we will explore the significance of AutoCAD, the benefits of mastering it efficiently, and provide a comprehensive guide to learning AutoCAD step-by-step.
Understanding AutoCAD Basics
AutoCAD Definition and Applications: AutoCAD is a CAD software that allows users to create precise 2D and 3D drawings. In architecture, it facilitates the design of buildings and structures. Engineers use it for mechanical, electrical, and civil engineering projects. Additionally, it finds applications in product design, interior design, and more.
User Interface and Essential Tools: Upon launching AutoCAD, users encounter a user-friendly interface with various tools and menus. Understanding the layout of the interface, tool palettes, and command line is crucial for smooth navigation.
Navigation and Orientation: Navigating within AutoCAD involves panning, zooming, and rotating the view. Learning how to efficiently navigate in the drawing area is essential to work effectively.
Setting Up AutoCAD for Success
Installation Guide: Well walk readers through the process of installing AutoCAD on their computers, ensuring they have access to this powerful software.
Initial Configuration and Customization: Configuring AutoCAD to suit individual preferences and needs can significantly enhance productivity. Well guide readers through the initial setup and customization of settings.
Hardware Requirements: AutoCAD is a resource-intensive software, and having the right hardware can greatly impact its performance. Well provide tips on hardware requirements for a smoother operation.
Learning the Fundamental Commands
Essential Drawing and Editing Commands: Mastering fundamental commands like line, circle, trim, and extend is essential for creating accurate and efficient drawings. Well introduce these commands and provide practical examples and exercises for better understanding.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them: Beginners often encounter common mistakes when using AutoCAD. Well discuss these errors and provide tips on how to avoid them to maintain a smooth workflow.
Mastering Advanced Techniques
Complex Drawing Tools and Commands: AutoCAD offers a wide array of advanced commands such as offset, array, and hatch. Exploring these tools will enable users to create intricate designs and streamline their workflow.
Utilizing Layers and Blocks: Organizing drawings using layers and blocks can significantly enhance efficiency. Well demonstrate how to utilize these features effectively.
Model Space and Paper Space: Understanding the concept of model space and paper space is vital for creating professional layouts suitable for printing.
Utilizing AutoCAD Resources
Reputable Online Tutorials and Forums: Well recommend trusted online tutorials and forums where users can access additional learning resources and connect with the AutoCAD community.
Official Documentation and Help Resources: AutoCAD provides comprehensive official documentation and help resources. Well emphasize the importance of utilizing these resources for effective learning.
Communities and User Groups: Being part of AutoCAD user groups and communities fosters knowledge sharing and troubleshooting assistance.
Enhancing Productivity with Shortcuts and Automation
Time-saving Keyboard Shortcuts and Command Aliases: Learning keyboard shortcuts and command aliases can significantly speed up the design process. Well introduce some of the most useful shortcuts.
Benefits of Macros and Scripts: Automating repetitive tasks using macros and scripts can save time and effort. Well discuss the benefits of using automation tools within AutoCAD.
Customizing Tool Palettes and Menus: Tailoring tool palettes and menus to individual needs can streamline the workflow and enhance productivity.
Learning from Real-world Projects
Practicing AutoCAD through Hands-on Projects: Hands-on projects offer practical experience and reinforce learning. Well encourage readers to undertake real-world projects to sharpen their skills.
Examples of Practical Projects: Well provide examples of practical projects relevant to readers interests, such as architectural floor plans and mechanical drawings.
The Importance of Persistence and Dedication: Learning AutoCAD requires dedication and practice. Well emphasize the importance of perseverance to achieve mastery.
Troubleshooting and Common Challenges
Identifying Common Issues and Troubleshooting: Well address common issues faced by beginners and provide troubleshooting tips to overcome them.
Dealing with Error Messages: AutoCAD may generate error messages during use. Well discuss common error messages and their solutions.
Preventing Data Loss and File Recovery: Data loss can be frustrating. Well share tips to prevent data loss and methods to recover files in case of accidental deletion.
How to Learn AutoCAD: tips
Learning AutoCAD can be a rewarding experience, and here are some tips to help you get started and make the most out of your learning journey:
- Start with the Basics: Begin by understanding the fundamental concepts of AutoCAD, such as the user interface, navigation, and basic drawing commands. Familiarize yourself with essential tools and functions before moving on to more advanced features.
- Utilize Online Resources: Take advantage of the wealth of online tutorials, videos, and courses available. Many websites and platforms offer free and paid resources for learning AutoCAD. These resources provide step-by-step guidance and practical examples.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering AutoCAD. Set aside dedicated time each day or week to work on projects, exercises, and tutorials. The more you practice, the more confident and proficient youll become.
- Work on Real-world Projects: Apply your skills to real-world projects that interest you. Whether its designing a floor plan or creating a 3D model, hands-on projects reinforce learning and make the experience more enjoyable.
- Join AutoCAD Communities: Engage with other learners and professionals in AutoCAD communities and forums. Participating in discussions, asking questions, and sharing knowledge can provide valuable insights and support.
- Explore Advanced Features: Once youve grasped the basics, venture into more advanced features and commands. AutoCAD offers a wide range of tools for complex designs and modeling. Dont be afraid to experiment and push your boundaries.
- Use Keyboard Shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with essential keyboard shortcuts. Using shortcuts can significantly speed up your workflow and make you more efficient in executing commands.
- Learn from Mistakes: Its normal to encounter challenges while learning AutoCAD. Embrace mistakes as learning opportunities and take the time to understand what went wrong. Learning from your errors will help you improve.
- Stay Updated: AutoCAD evolves with new updates and features. Stay informed about the latest developments in the software and explore new functionalities to expand your skillset.
- Stay Motivated: Learning a new software can be challenging, but stay motivated and persistent. Set clear goals, track your progress, and celebrate your achievements along the way.
Remember that learning AutoCAD, like any new skill, takes time and patience. Be kind to yourself and enjoy the process of discovering the possibilities that AutoCAD offers for design and creativity. With dedication and practice, youll soon become proficient in this valuable tool.
Product Development using AutoCAD
By the end of this 1-hour long project-based course, you will be able to design and draw 2D products customized to fit your needs using AutoCAD Design. Throughout the project, you will be equipped with the fundamentals of AutoCAD design, you will be able to draw lines and basic shapes . Afterwards, you will learn how to modify those shapes according to your product drawings.
At the end, you will apply all this to create a 2D spinner drawing. Learning AutoCAD and being professional at it allows you to design a wide range of products, opens up freelancing opportunities for product design and lastly an asset that can be added for your design skills set.Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. Were currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.
AutoCAD practice drawings with PDF eBook
AutoCAD practice drawings with PDF eBook
Updated on June 11, 2024 | By Jaiprakash Pandey | Category AutoCAD | min reading time
Disclosure: Our content is supported by readers like you, we earn commission from affiliated products you buy from links placed on our website without any extra cost to you. This does not influence our content recommendations. Learn more about our affiliate process here.
2D and 3D practice drawings and projects
Get our collection of more than 100 fully dimensioned 2D and 3D practice drawings and projects
The best way to practice AutoCAD skill is with AutoCAD practice exercises, the more your practice the better you get at making drawings using AutoCAD.
So, to help you practice I have created this article with ten 2D and ten 3D drawings that you can make using AutoCAD or any other CAD software as well.
To get the full list of 2D and 3D practice drawings download the PDF eBook which contains more than 70 drawings fully illustrated with dimensions.
Click the download button above to get your eBook.
37lessons|IntermediateLevel
Practice your 2D AutoCAD drawing skill using with the collection of fully dimensioned drawings.
2D drawings
Use AutoCAD, BricsCAD, ZWCAD or any other similar CAD software to make these drawings.
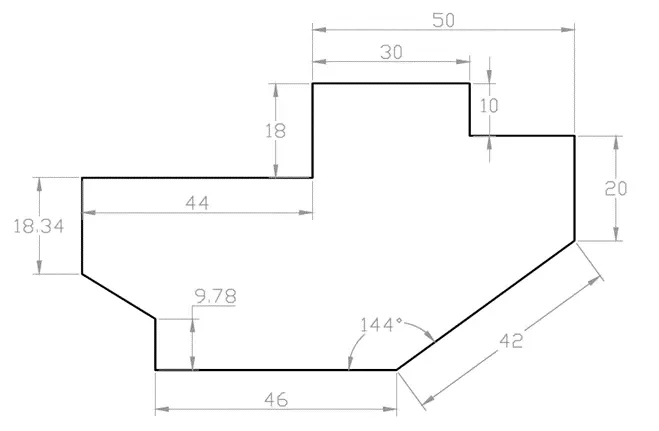
2D practice drawing 1
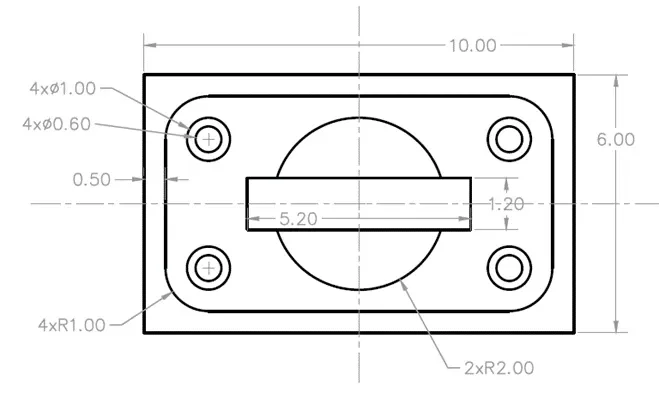
2D practice drawing 2
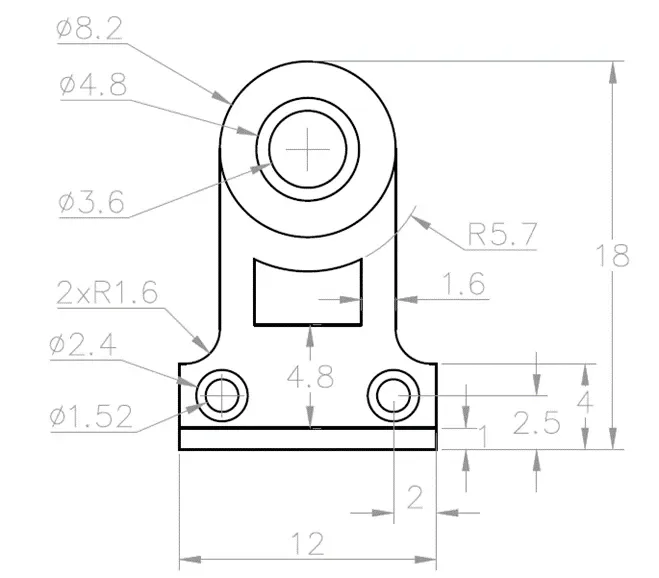
2D practice drawing 3
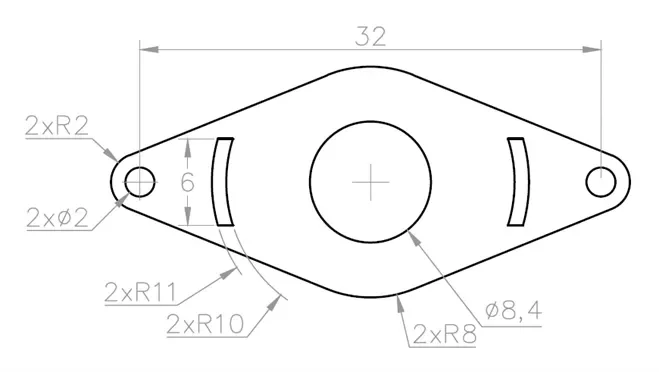
2D practice drawing 4
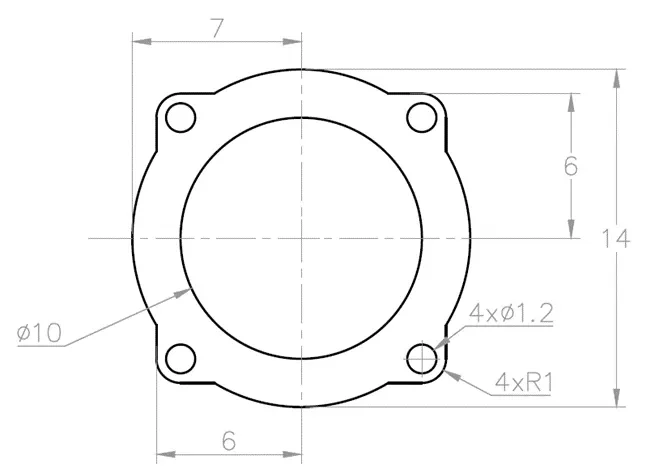
2D practice drawing 5
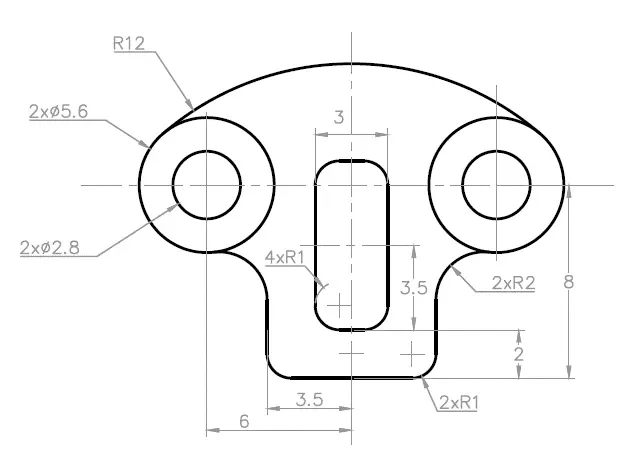
2D practice drawing 6
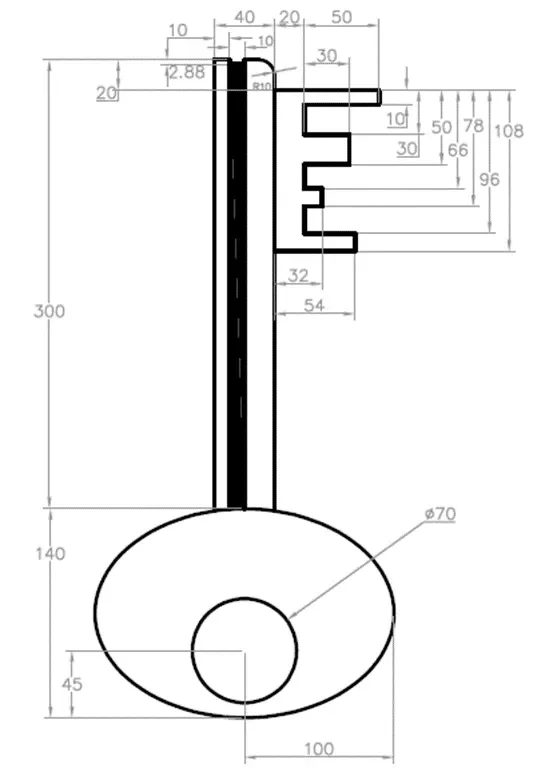
2D practice drawing 7
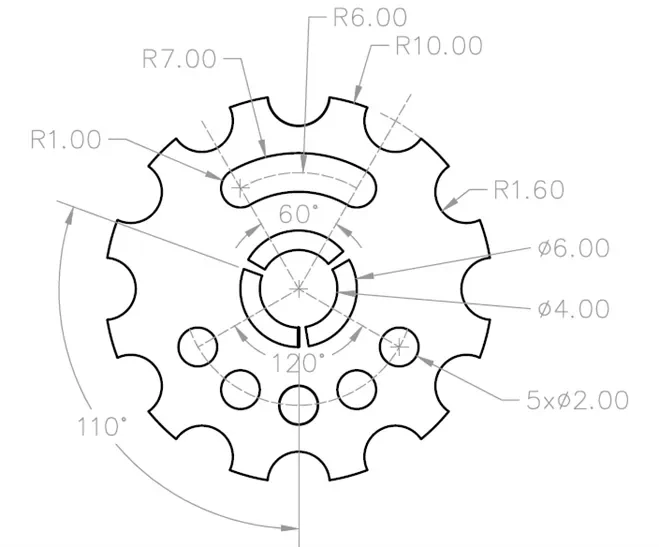
2D practice drawing 8
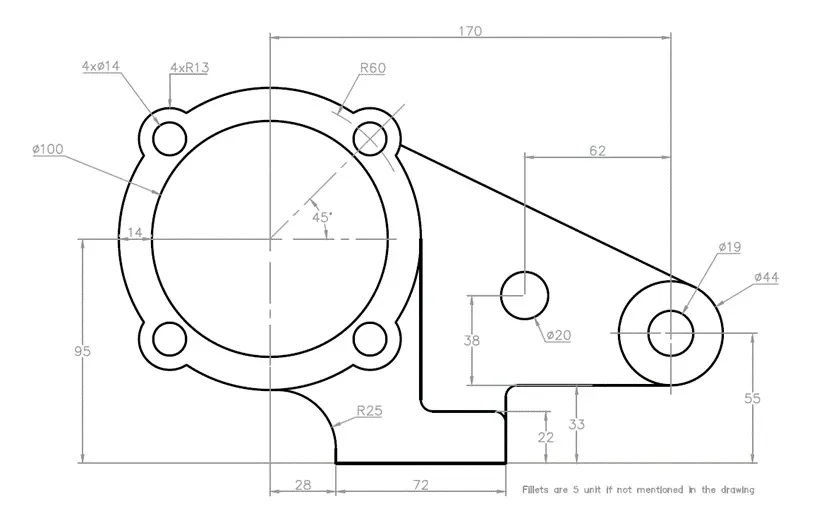
2D practice drawing 9
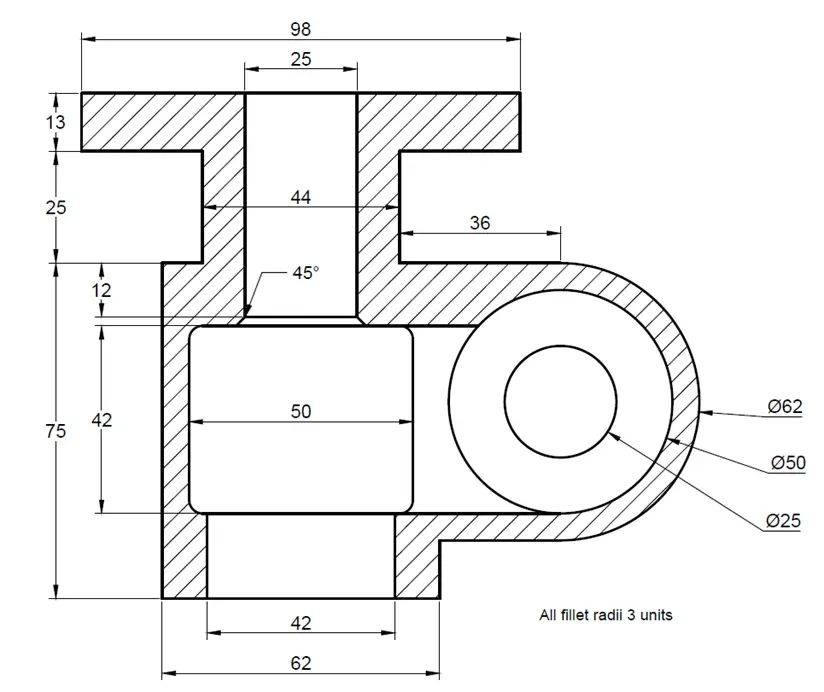
2D practice drawing 10
34lessons|IntermediateLevel
Practice your AutoCAD skill with real world 3D drawings from different engineering disciplines.
3D Drawings
You can use AutoCAD, BricsCAD, ZWCAD, Solidworks, Fusion 360 or any other software with 3D workspace to practice these drawings.
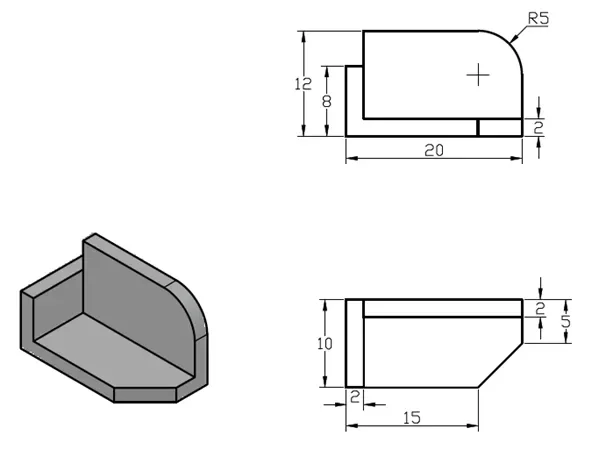
3D practice drawing 1
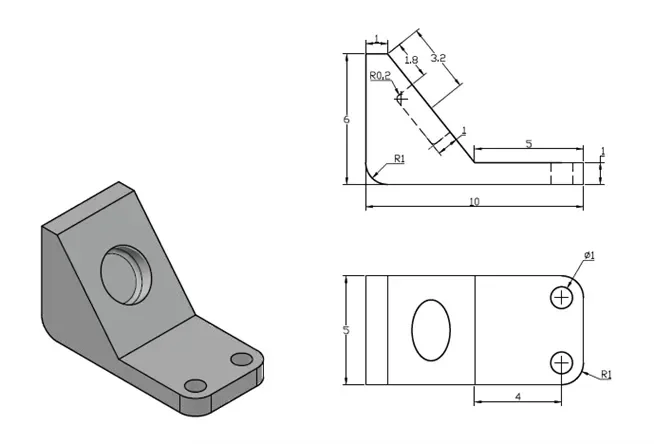
3D practice drawing 2
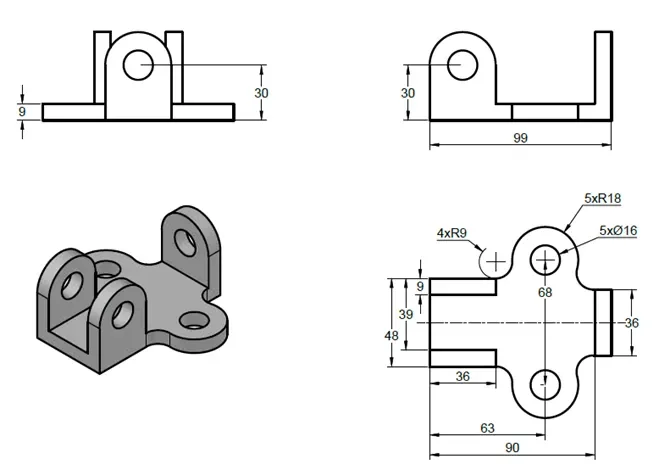
3D practice drawing 3
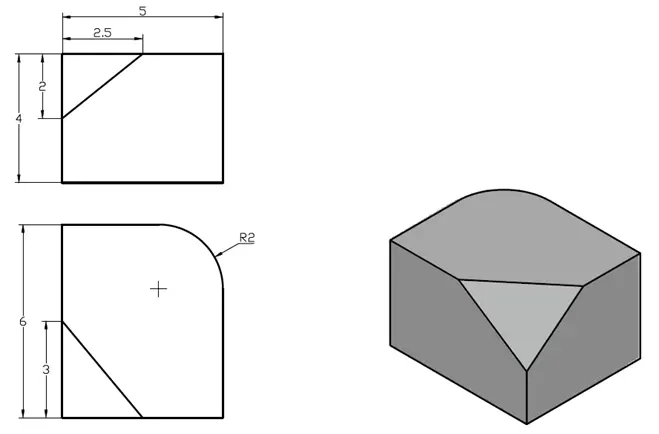
3D practice drawing 4
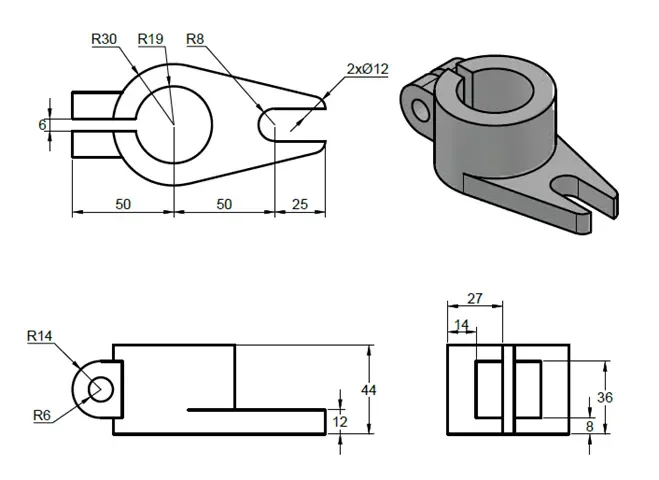
3D practice drawing 5
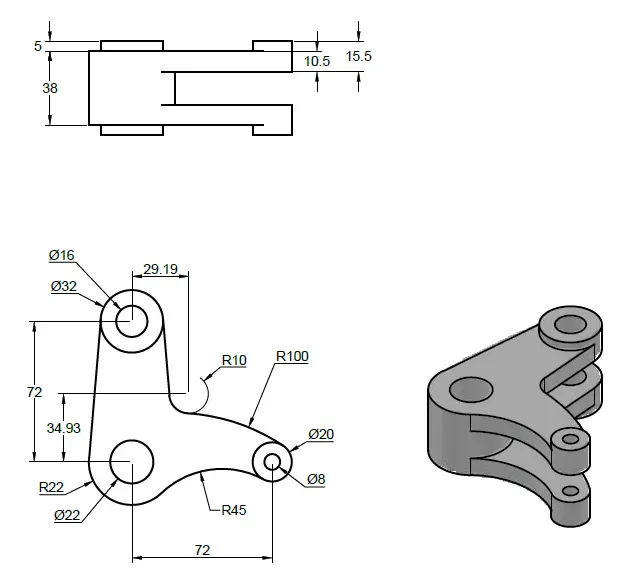
3D practice drawing 6
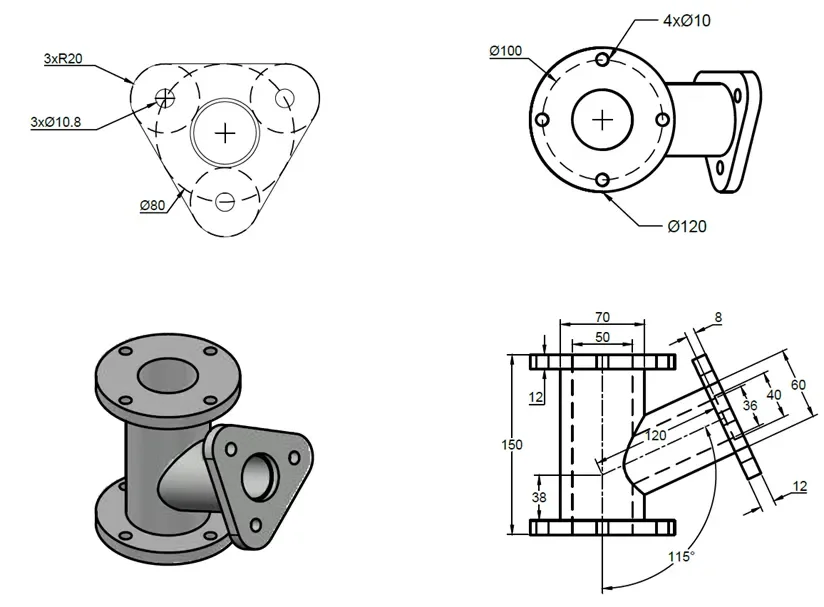
3D practice drawing 7
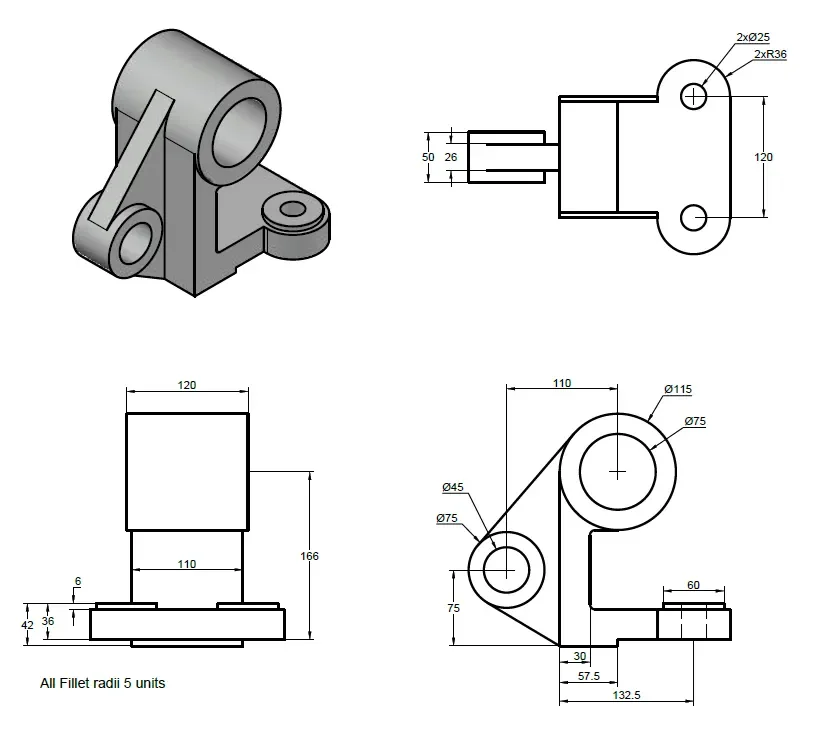
3D practice drawing 8
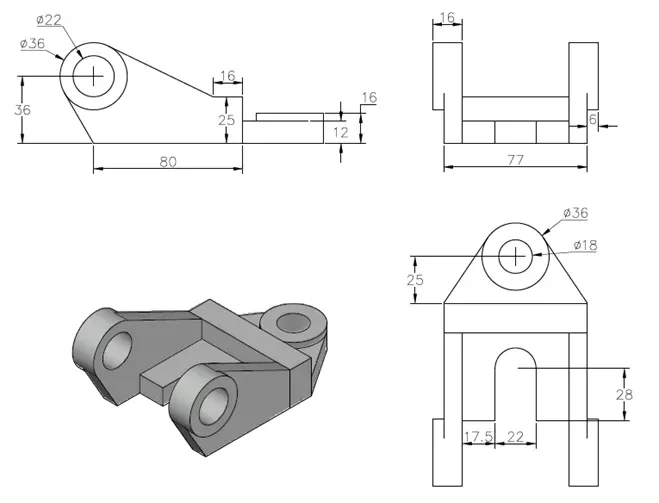
3D practice drawing 9
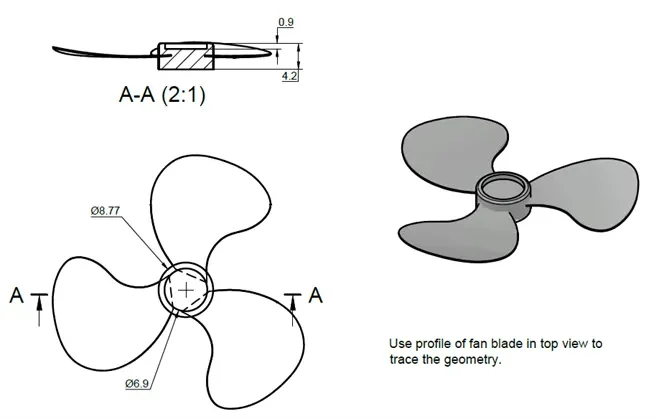
3D practice drawing 10
Summary
These practice drawings are part of our collection of nearly 100 2D and 3D practice drawings from our practice drawing eBook.
You can get this eBook for free using the download bar at the top of this page.
Disclosure: On this site, we have placed some recommended products and services from which we get an affiliate commission for every purchase you make without any extra cost to you. Learn more about our affiliate process here.
Jaiprakash Pandey is the published author of Practical AutoCAD book by Packt publication he is also an Autodesk AutoCAD certified professional and Autodesk expert elite community. He has been delivering CAD training to corporate clients for more than 8 years and his clients include Steel, Power, Automobile industries and also government organizations, fortune 500 companies and the military.
Get SourceCAD Free Courses
Start learning your CAD and engineering tool for free with our free courses and eBooks. Get a certificate of completion on finishing the courses.
Getting started with AutoCAD
You can create a lot of different types of geometric objects in AutoCAD, but you only need to know a few of them for most 2D drawings.
Tip:If you want to simplify the display while you create geometric objects, press F12 to turn off dynamic input.
Lines
The line is the most basic and common object in AutoCAD drawings. To draw a line, click the Line tool.
Alternatively, you can type LINE or just L in the Command window, and then press Enter or the Spacebar.
Notice the prompt in the Command window for a point location.

To specify the starting point for this line, you would type in the Cartesian coordinates 0,0. It's generally a good idea to locate one corner of your model at 0,0, which is called the origin point. To locate additional points, you could specify additionalX,Ycoordinate locations in the drawing area, however more efficient methods for specifying points are available, and will be presented in the Precision topic.
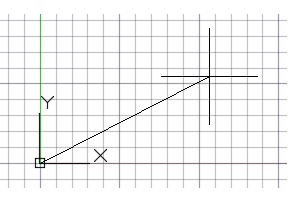
After you specify the next point, the LINE command automatically repeats itself, and it keeps prompting you for additional points. Press Enter or the Spacebar to end the sequence.
Grid Display
Some people like working with grid lines as a reference, while others prefer working in a blank area. To turn off the grid display, press F7. Even with the grid turned off, you can force your cursor to snap to grid increments by pressing F9.
Lines as Construction Aids
Lines can serve as reference and construction geometry such as
- Property line setbacks
- The mirror line of a symmetrical mechanical part
- Clearance lines to avoid interferences
- Traversal path lines
Circles
The default option of the CIRCLE command requires you to specify a center point and a radius.
Additional circle options are available from the drop-down:
Alternatively, you can enter CIRCLE or just C in the Command window and click to choose an option. If you do, you can specify a center point, or you can click one of the highlighted command options as shown below.

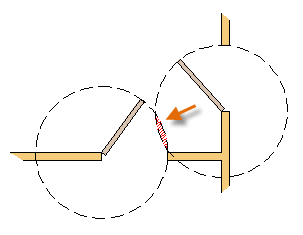
Circles can be useful as reference geometry. For example, you can see that the two doors in the illustration can interfere with each other.
Polylines and Rectangles
A polyline is a connected sequence of line or arc segments that is created as a single object.
Use the PLINE command to create open or closed polylines for
- Geometry that needs to have fixed-width segments
- Continuous paths for which you need to know the total length
- Contour lines for topographic maps and isobaric data
- Wiring diagrams and traces on printed circuit boards
- Process and piping diagrams
Polylines can have a constantwidthor they can have different starting and ending widths. After you specify the first point of the polyline, you can use the Width option to specify the width of all subsequently created segments. You can change the width value at any time, even as you create new segments.
Here is an example of a printed circuit board in which the traces were created with wide polylines. The landing pads were created with the DONUT command.
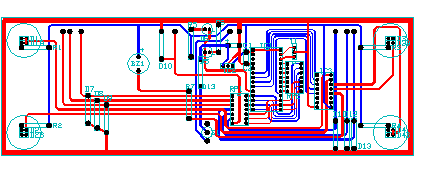
Polylines can have different starting and ending widths for each segment as shown here:
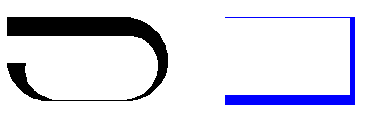
A fast way to create closed rectangular polylines is to use the RECTANG command (enter REC in the Command window).
Simply click two diagonal points for the rectangle as illustrated. If you use this method, turn on grid snap (F9) for precision.

The User Coordinate System (Optional)
The user coordinate system (UCS) icon indicates the direction of the positive X and Y axis for any coordinates that you enter, and it also defines the horizontal and vertical directions in a drawing. In some 2D drawings, it can be convenient to click and place the UCS to change the origin point and the X or Y axis.
For example, by reorienting the UCS, you can create rectangles that are automatically aligned with the X axis as shown.
To restore the user coordinate system to its original location, enter UCS in the Command window and press Enter to specify the default <World> option.
Hatches and Fills
In AutoCAD, a hatch is a single, compound object that covers a specified area with a pattern of lines, dots, shapes, a solid fill color, or a gradient fill.
When you start the HATCH command, the ribbon temporarily displays the Hatch Creation tab. On this tab, you can choose from more than 70 industry-standard imperial and ISO hatch patterns, along with many specialized options.
The simplest procedure is to choose a hatch pattern and scale from theribbon, andclick within any area that is completely enclosed by objects. You need to specify the scale factor for the hatch to control its size and spacing.
After you create a hatch, you can move the bounding objects to adjust the hatch area, or you can delete one or more of the bounding objects to create partially bounded hatches:
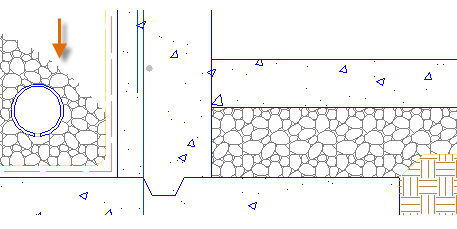
Tip:If you set a hatch pattern to be a solid or gradient fill, also consider setting a transparency level on the Hatch Creation tab for interesting overlap effects.
Here are some examples of how you can use solid-fill hatches:
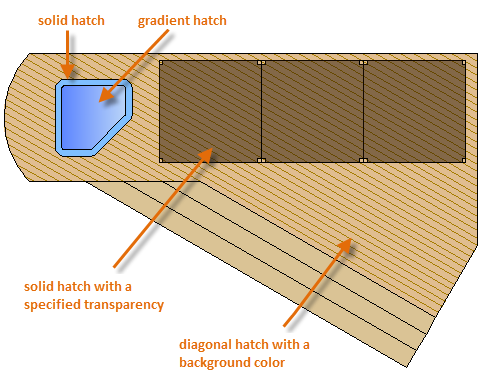
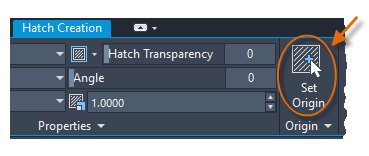
Tip:If you need to align the pattern in a hatch, which might be the case with the decking boards above, use the Set Origin option to specify an alignment point.
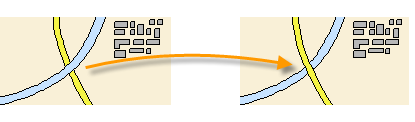
For overlapping hatches, fills, wide polylines, and text objects, use the DRAWORDER command to determine which objects are on top or below the others. For example, you probably want the yellow highway to cross the blue river rather than the other way around.
You can access several draworderoptions from the Modify panel on the ribbon. Click to expand the Modify panel, and then click the down-arrow as shown below.
The drop-down list displays options for selected objects plus additional options that apply to all objects of a certain type, such as text.