How to Fix Slow Internet Speeds on Your Home Network

8 Fixes for Slow WiFi on Your Home Network
Youve paid for a fast-speed internet connection and youre entitled to a decent connection speed. However, the problem could be with your home network, so its not something your ISP can fix. If youre on a low-speed plan, though, there are still a few ways to increase your internet speed.
In this guide, were going to show you how to increase Wi-Fi speed. Before we get down to business, check if the issue is device-specific. If the Wi-Fi speed is slow only on one of your devices, the problem could be with your device rather than the network. If the Wi-Fi speed is slow across all your devices, try the following fixes.
Also, we created a short video going over some other reasons and fixes for slow internet, so be sure to check it out here on our YouTube channel:
1. Reboot the Modem
Most modern routers dont require regular reboots. However, a reboot could give the router a chance to cool off and start afresh. This is why this is the first solution you should try to increase Wi-Fi speed on your home network.
Some routers come with a built-in reboot scheduler. Plus, both Tomato and DD-WRT allow you to set automatic reboots. Schedule a reboot for the middle of the night so your internet connectivity isnt disrupted during the day.
2. Enable Quality of Service (QoS) on Your Router
Bandwidth intensive activities can slow down your Wi-Fi speed. For instance, have you tried to download the Windows 10 ISO or any other large files?
When the download is running, it leaves less bandwidth for other tasks, effectively slowing down your Wi-Fi. Often, it could be other network users that are running some bandwidth-heavy tasks. Check with your siblings or roommate if theyre streaming Netflix or gaming.
If they are, you dont have to be at their mercy to get some decent Wi-Fi speed. You have the option to enable Quality of Service (QoS) from your routers firmware and prioritize the networks traffic.
If someone on your network frequently downloads movies, sparing you little bandwidth, go to your routers firmware and set up QoS. Most routers have QoS under advanced settings, but some may use a different name for it.
TP-Link, for example, calls it Bandwidth Control where you can add Controlling Rules. This is essentially QoS, but with a different name.
3. Scan Background Programs Network Usage
If you dont think other users are hogging any of your Wi-Fi bandwidth, see if any programs are running in the background on your PC. A lot of programs frequently check for updates or perform other network-oriented tasks.
Open the Task Manager and switch to the Processes tab. Check the Network column and look for processes that have been taking up an unexpected volume of bandwidth. Stop those processes and see if the Wi-Fi speed improves.
There are, of course, more ways to check which programs are using your bandwidth.
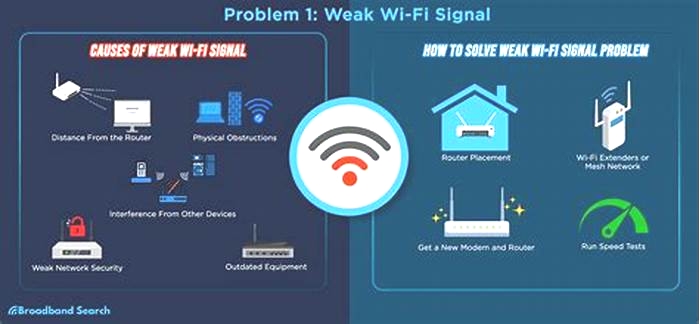
4. Change the Routers Position
The routers position plays a significant role in your Wi-Fi networks performance. When you buy a router, you probably set it up wherever you found the closest power outlet near your desk. However, positioning your router warrants some extra thought if youve been experiencing slow Wi-Fi speeds.
As a rule of thumb, always place your router up high and at the center of your home. Wi-Fi signals are broadcasted in all directions, so it doesnt make sense to tuck the router away in a corner. Even worse is to put the router closer to the ground. Instead, place the router closer to the ceiling to minimize interference from household objects and extend the routers range.
If your home is rather large, consider investing in an antenna or powerline adapters. Recently, though, it has become increasingly common for home users to set up mesh networks instead of powerline adapters or access points.
You could also use an old router as a repeater to extend the Wi-Fi range. On a TP-Link router, you can change your router settings to make it function as an Access Point from Advanced > Operation Mode.
5. Change Your Router Band
If youre like most users, you unboxed your router, installed it, and never looked back. This means you probably didnt notice that you have the option to change your routers broadcast frequency bands. Unless you own an ancient router, you have the option to choose between 2.4GHz and 5GHz channels.
Most household electronics use the 2.4GHz spectrum which can lead to a lot of crowding. For instance, your Microwave oven operates at a 2.45GHz frequency. A 2.4GHz channel on your router broadcasts between 2.412GHz and 2.472GHz, which means the Microwave oven could disrupt your connection.
It isnt just microwave ovens, though. Everything from a cordless phone to other Wi-Fi routers, and even your Christmas lights, can interfere with the 2.4GHz Wi-Fi band.
This interference can cause your Wi-Fi speeds to slow down. If your router has the 5GHz band, make the switch to see if it increases your Wi-Fi speed. If you have a 2.4GHz-only router, try the next fix.
6. Switch to a Different Channel
Almost every house has a Wi-Fi network. This means whether you like it or not, your neighbors are sharing your signal space. Crowded channels are particularly an issue in crowded neighborhoods with plenty of routers around.
However, crowded channels are mostly a 2.4GHz phenomenon. If your router can broadcast or receive only a 2.4GHz signal, this can be a problem because your router only has 14 channels for transmission.
Change the channel to 1, 6, or 11 if your router uses a 2.4GHz band. They are your best bet since they dont overlap. If your router can broadcast a 5GHz wireless signal, you have a lot more channels to choose from.
Channel selection isnt something you will need to spend a lot of time on if your router uses the 5GHz band. Any channel on a 5GHz band should work well, except DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection).
7. Update Router Firmware
Many newer routers update automatically. If yours doesnt, it would be worth your while to go to the updates page and see if an update is due.
A firmware update probably wont have a monumental impact on your Wi-Fi speed. However, if you havent run an update in a while, you may see a noticeable improvement in your Wi-Fi speed after the update. Plus, you also make your router more secure if the manufacturer has rolled out security updates.
You may even choose to flash custom firmware such as DD-WRT or Tomato. Go to either DD-WRT or Tomatos website and search for your routers model number. Download the .bin file and look for a section called Firmware Upgrade or something similar. Browse the .bin file and upgrade.
8. Purchase and Install a New Router
If none of these fixes could increase slow Wi-Fi speed on your home network, now is a good time to bring home a new router. A lot of home users never bother much with routers. They continue to use the one provided by their ISP for years.
ISPs focus on cost minimization rather than performance. This is why ISP-provided routers are generally basic. Bring home a modern router to not just increase your Wi-Fi speed, but also improve overall performance.
Did You Fix Your Slow Wi-Fi?
Hopefully, one of these fixes helped you improve slow Wi-Fi on your home network. If youve signed up for a high-speed internet plan with your ISP, in most cases, the Wi-Fi speed is slow because of your router.
While these fixes should work well enough, wired connections are more stable and faster. If youre going to jump on an extremely important video call, its smart to use a wired connection.
Why is my Internet connection so slow?
No matter how fast your Internet connection is, there are times when things will slow down to a crawl. This article will help you sort out what kinds of things can go wrong, learn what you can do about them, and discover how to get the most from your Internet connection.
Windows provides a built-in troubleshooter that can automatically find and fix some common connection problems.
Open the Internet Connections troubleshooter by clicking theStartbutton 
The type of connection you have makes a difference
The type of Internet connection you use is the most important factor in determining your connection speed. The three most common ways to connect to the Internet from home are dial-up, DSL, and cable. If you have a choice, cable is usually the fastest, but both DSL and cable are faster than dial-up.
Many Internet providers also offer Fiber Optic Service (FiOS), which connects to the Internet using light over an optical network. In your home, you still connect your computer through copper wiring. The advantage of FiOS is that it can provide higher speeds than traditional copper wire connections such as DSL or cable. Some Internet providers offer multiple options, depending on the area you're in. More populated areas are more likely to have FiOS available. Check with your phone company or Internet provider for more information.
If you use a dial-up connection, there are a couple of good ways to optimize your Internet speed. First, use the fastest modem you can. The fastest modem you can use will send and receive information at a rate of 56 kilobits per second (Kbps). You won't get a full 56 Kbps speed most of the time, but with a good phone line, you should approach at least 45-50 Kbps.
Second, make sure that your phone line is in good condition. If the telephone wiring in your home or business is old or deteriorating, you might be picking up stray signals or cross talk from other phone lines. These problems will slow your Internet connection because the modem will have to send the same information over and over until it's transmitted without interruption. Check your telephone wires to be sure they aren't damaged, frayed, or twisted around power or other telephone cables. If you notice crackling in your phones, you might want to contact your phone provider to have them check the lines inside and outside your home to make sure they are in good condition.
Tips for wireless network users
When you're connecting to a wireless network (WiFi), your Internet connection speed can be affected by both where your computer is located and whether other wireless devices are in the same area. Wireless networks operate on frequencies that are similar to those used by other devices, such as microwave ovens or cordless phones. Operating a 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) cordless phone next to your 2.4 GHz wireless laptop can cause interference, or completely block the wireless network connection. If you want to make phone calls while surfing the web, either use a wired telephone or a cordless phone that operates at a different frequency than your wireless network.
Proximity to the wireless access point or router, as well as physical obstructions, can affect the quality of your Internet connection. To improve your connection speed, move closer to the access point and make sure that there are no physical obstructions between the access point and your computer.
Computer woes: spyware, viruses, and other programs
The health of your computer can affect your Internet connection. Spyware and viruses can definitely cause problems, but your Internet connection speed can also be affected by add-on programs, the amount of memory the computer has, hard disk space and condition, and the programs that are running.
Two of the most frequent causes of poor Internet performance are spyware and viruses. Spyware can slow your system by interfering with your browser and monopolizing your Internet connection. Spyware monitors your Internet use and keystrokes, which adds delays. The problem is compounded when there are multiple spyware programs running at the same time. If the problem is severe enough, you can lose connectivity altogether. To get your Internet performance back, you should regularly run an antispyware program to clean out any spyware infestation.
Computer viruses can also cause poor Internet performance. When a virus infects a computer, it installs computer code which will attempt to propagate itself, usually by sending copies of itself through email. Some viruses can multiply at the rate of hundreds of email messages per minute, which leaves little computing power and Internet connection bandwidth for anything else. Viruses often don't give any obvious indication that they're running, so it's best to run your antivirus software at all times.
Browser add-ons also cause performance problems. Browser add-ons are programs, such as multimedia add-ons, search bars, or other programs that usually appear on your browser's toolbar. Many browser add-ons can add to a rich browsing experience, offering multimedia or specialized document viewing. However, some add-ons can slow your Internet connection. If you suspect that add-ons are causing slow performance, try starting InternetExplorer in Add-ons disabled mode. Add-ons are disabled only for the session, but if you find your performance improves, you can use the Add-on Manager to turn them off permanently. To access the Add-on Manager from InternetExplorer, click theToolsbutton, and then clickManage Add-ons.
Like all computer programs, InternetExplorer requires a certain amount of computing power, memory, and disk space to run efficiently. Every webpage you view is first downloaded to memory and then saved to temporary disk files. Running another program that's using lots of memory and computing power can compete with InternetExplorer and cause delays. If you find your Internet connection running slowly and you have other programs running, try closing them. If you want to run several programs, consider increasing the memory you have on your computer. Low disk space can also cause performance problems. You can increase your disk space by deleting InternetExplorer's temporary files.
Occasionally, settings get changed in InternetExplorer that could possibly affect how InternetExplorer works. You can reset InternetExplorer to its default settings. Resetting InternetExplorer isn't reversible, so you should read the list of settings that are affected before resetting.
Outside factors that affect connection speeds
Unfortunately, there are events and conditions that are outside your control. Even with a fast connection, external factors, such as busy websites or spreading computer viruses, can slow the entire web. Popular websites can become overwhelmed with users. For example, when a television commercial mentions a website, many people might try to visit the site at the same time. If the website isn't prepared to handle the traffic, you might encounter delays.
During times of heavy computer virus outbreaks, the Internet can slow down. Many viruses spread by causing computers to send out hundreds or thousands of copies of the virus. This can slow the Internet by sheer volume. You can see what major outbreaks are currently happening by visiting your antivirus vendor's website, or theSecurity at Homewebsite.
Local Internet congestion can also result in slower-than-normal connection speeds. These slowdowns occur when many people try to connect to the Internet at the same time, and they occur most often at peak activity times, such as after school hours when students get home and connect to the web.
If you're on a corporate network, general network and proxy server use can affect your Internet performance. Most network administrators monitor Internet use, and will try to keep people from doing things like downloading large files during peak hours. If you find that your Internet access is slow at times, you might discuss it with your network administrator.