Guide to Optimizing Your Router Settings for Gaming

MakeUseOf
When playing games online, your router has an effect on your experience. Your connection speed goes to waste if you have a junky router that can't keep up or keep you connected.
If you're experiencing disconnects, lag, or other online gaming problems, check out these best router settings, tips, and tweaks for gaming.
Why Gaming Routers Are Unnecessary
A gaming router is one that's specifically designed to optimize network settings for the best gaming experience possible. Or at least, that's what marketers want you to think. They want to convince you that gaming routers offer something that normal routers don't, in the hopes that you'll pay more money for a better-quality connection.
While gaming routers may have been superior in the past, there's really no reason you must use them anymore. While they may offer some useful features, like extra Ethernet ports and more powerful antennas, these aren't necessary for casual players. This is especially the case if your gaming system is the only device using bandwidth in your home.
As it turns out, most modern routers, even basic ones, support the features necessary for a smooth gaming session. That doesn't mean you should go for a super-cheap router, though. A $20 model might have the right specs on paper, but likely won't be reliable in day-to-day use and won't last long.
If after shopping around, you find that the best value is a gaming router, then go ahead and buy it. Just keep in mind that a router marked as "for gaming" doesn't necessarily make it better. If you can find a respectable non-gaming router with the right specs, it should more than suffice.
Now let's look at how to optimize your router for gaming using the following options and features. These will help you minimize network issues, maximize performance, and hopefully get interruption-free gaming sessions.
1. Enable Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service is a router feature that prioritizes data packets for specific connected devices. It comes in handy when you have multiple users on the network all doing network-intensive activities.
For example, if your spouse is watching 4K Netflix while your son is video chatting with his friend and downloading a huge amount of data in the background, that will all hog a lot of bandwidth. When you try playing a game with all this going on, there won't be much bandwidth left, resulting in lag and poor performance.
With QoS enabled, you can prioritize your gaming PC or console over other devices using the network. This forces your router to handle gaming data first before worrying about everything else. To learn more, see our guide to setting up QoS on routers.
2. Use Gigabit Ethernet Ports
When gaming, if at all possible, you should always prefer Ethernet over Wi-Fi. While gaming on strong Wi-Fi is usually good enough, it sacrifices speed and latency for the convenience of being cable-free.
To ensure future-proofing and maximum performance, you should use a router with gigabit Ethernet ports. Gigabit Ethernet can handle speeds up to 1,000Mbps, assuming your connection can deliver those speeds. If you have multiple gaming systems, look for a router with more ports so you don't have to buy a switch separately.
If your router is far away from your gaming machine and you can't run a cable, try using powerline adapters. These let you transfer internet data through the normal power outlets in your home. They come in pairs: plug one in near your router and the other one near your console or PC, then use an Ethernet cable to connect the adapters to your router and system. While they're not as reliable as true Ethernet, it's an easy way to get Ethernet across rooms and is better than Wi-Fi.
3. Use Modern Wi-Fi Standards
If Ethernet isn't an option, then you should make sure to get a router that supports current wireless standards. On most routers, you'll see a value such as AC2600 or AX1500, which tells you the standard it uses and its theoretical maximum speed.
AC, or Wi-Fi 5, is common on routers in 2020. But AX, or Wi-Fi 6, is becoming the new standard. Wi-Fi 6-compatible devices aren't widely available at the time of writing; none of the current-generation consoles support it. So if you're looking for a new router, buying a Wi-Fi 6 model will future-proof you, but Wi-Fi 5 is still suitable for now.
Almost every modern router is dual-band, meaning it supports both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. 5GHz networks are more reliable than the older 2.4GHz band, but have a downside of a shorter range.
Some older devices only support 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, but you can take advantage of 5GHz with newer devices, making a dual-band model vital. If you have to use Wi-Fi for gaming, use the 5GHz band if your system supports it.
In a small apartment, you don't have to worry about the shorter range. But in a large house, try to rearrange your setup so that the router isn't more than a room away from your gaming device.
4. MU-MIMO
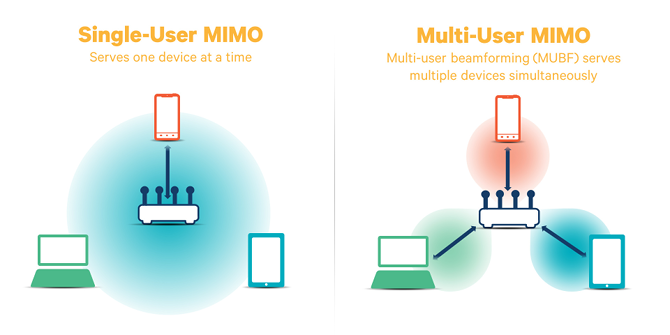
MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output) is an important feature if your network serves many different devices. As mentioned above, it's common for multiple users to use high-bandwidth applications while you try to play games.
Without MU-MIMO, your router has to serve each device one by one, which can reduce overall network speed. With MU-MIMO, the router sets up multiple "mini-networks" and works with each device simultaneously. You can learn more about this in our overview of MU-MIMO.
5. Optimize Your Wireless Channel
One of the main reasons to avoid Wi-Fi when gaming is that Wi-Fi signals can interfere with each other. When a signal meets interference, it fails to reach its destination and has to resend the data. With enough interference, latency and packet loss will increase, affecting your game.
Interference can occur on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, but it's far more common when using 2.4GHz. The 2.4GHz band can only broadcast on 11 channels in the US, and only three of them are non-overlapping. Because the 2.4GHz band is close to what other common household devices use, like microwaves and baby monitors, you can pick up interference even from non-Wi-Fi devices.
In contrast, the 5GHz band has 23 non-overlapping channels. The more broadcasts on a channel, the greater the congestion---meaning that there's more space on 5GHz networks in physically crowded spaces.
Regardless of which band you use, you should definitely analyze your Wi-Fi network, find which channel is least-used, and manually set your router to use that channel. This should help with interference and congestion.
6. Have Sufficient CPU and RAM
CPU and RAM are important considerations when choosing computers and mobile devices, but you probably don't think about it for your router. And while routers don't have to run resource-intensive apps like Photoshop, they do have to handle tons of network data constantly.
If your router's CPU is weak, it may not be able to keep up with heavy network demand. Games don't usually send a whole lot of data on their own, but once you add in the constant data influx of video streams, file downloads, video chat, and other usage from multiple connected devices, a weaker router could struggle under the load.
If your computer and smartphone are the only devices on the network, you may be able to get away with a cheaper router. But if you have dozens of tablets, laptops, other smartphones, smart TVs, and various other IoT devices, then a fast CPU should be a priority.
7. Schedule Reboots
When something goes wrong with a device, you probably know what troubleshooting step to take first: turn it off and on again. This is especially true for older routers, which can suddenly drop connections and freeze for seemingly no reason.
For this reason, you can remove some headaches by automating a router reboot schedule. Some routers have this built-in; if you don't, switching to a custom router firmware may grant you the option. Otherwise, you can always buy a programmable timer switch to plug your router into.
8. Universal Plug-and-Play
UPnP, or Universal Plug and Play, is a common feature on routers that simplifies the process of port forwarding for you. If you're not aware, various internet protocols communicate over different ports, which your router uses to determine which devices traffic should go to.
Online games use many different ports; if you have trouble using voice chat in a particular game, you probably need to forward the port on your router so it knows where to send that traffic.
UPnP automatically forwards ports as they're needed by various devices on your network. Enabling this is convenient, as it prevents you from having to mess with ports every time you play a new online game.
However, using UPnP is a potential security risk for your router, as it could let malicious activity through to your network. It's up to you to decide whether the convenience is worth it.
What Router Features Affect Gaming Online?
It's important to understand what aspects of your router and home network actually affect online gaming.
A blazing-fast network speed is not vital for good performance in online games. Speed mostly affects downloading game updates in a timely manner (and having enough bandwidth on a crowded network, as discussed earlier). Once you have a game downloaded, you can have fine performance with it on a slower connection---as long as it's stable.
The most important aspect is the stability of your connection to the game server, which most games show as your latency or ping. While a powerful router might offer a fast and stable connection from your game console to your modem, it doesn't really affect the connection from your system to the game server. If your ISP is unreliable, you might end up with a poor connection even with a top-of-the-line router.
For most home users with average internet connections, you'll usually see somewhere between 50 and 100ms ping in online games (depending on how close you are to the servers). That's well below the average reaction time of most humans, meaning that dropping your ping down to something like 30ms would have little benefit.
In short: router features that help you prioritize traffic to your gaming device are most useful on busy home networks. With a simple one gaming device setup, high ping is the result of an unstable connection to the game server.
The Best Router Settings for Gaming
Now you know some of the router features you can use for a better gaming experience, or ones to look for next time you buy a router. You don't need a $500 gaming router that looks like something from a sci-fi movie for a solid gaming experience; you just need a reliable model with the features that matter for gaming.
If you need a new router, check out the best reliable Wi-Fi routers. And keep in mind that factors other than your network come into effect for gaming performance, especially when playing on PC. Have a look at how to optimize Windows 10 for gaming.
The best router settings for gaming
Online gaming is awesome. Teaming up with friends who may be physically located all over the world is great. Engaging with hundreds of other people in a virtual world is fantastic. Having that fun disrupted by network lag, connection latency, and random disconnects isveryuncool.
While an internet connection is often subject to the whims of your internet provider, there are still many things you can do with your local router and network setup to optimize your gaming experience. Lets dig in, starting from the top.
Use a capable router
Many home internet providers provide a combined modem and router device that you might be using for your home network and Wi-Fi. Some of these ISP-supplied routers do offer the type of control and software adjustments that are outlined below, but many do not. With that mind, if youre not already using your own router to manage your home network, you may want to.
A router is a type of computer. Just like any other computer, a router has processing and memory hardware that is handling all of the connections coming in and out of it. The more devices you have connected to your router, the more robust your router needs to be in order to handle the network effectively. Youll need to consider every device that connects to the router directly via wired or wireless connections, such as computers, laptops, cell phones, tablets, smart TVs, game consoles, connected doorbells, digital assistants, smart thermostats, Wi-Fi light bulbs, and so on. A simple router will have a hard time keeping up with so many connected devices, resulting in notable impacts to speed and connectivity.
Physical specifications are much like those of a PCyoull want to look for routers that have more processing power and more RAM. These specs might be difficult to locate for some router models, but there is marketing jargon that may help you identify higher-quality hardware, such as MU-MIMO, Wi-Fi 6 or AX support, and multi-gigabit LAN or WAN ports. Our guide to the best mesh Wi-Fi routers can also help point you in the right direction if youre looking to ditch your Internet providers networking gear.
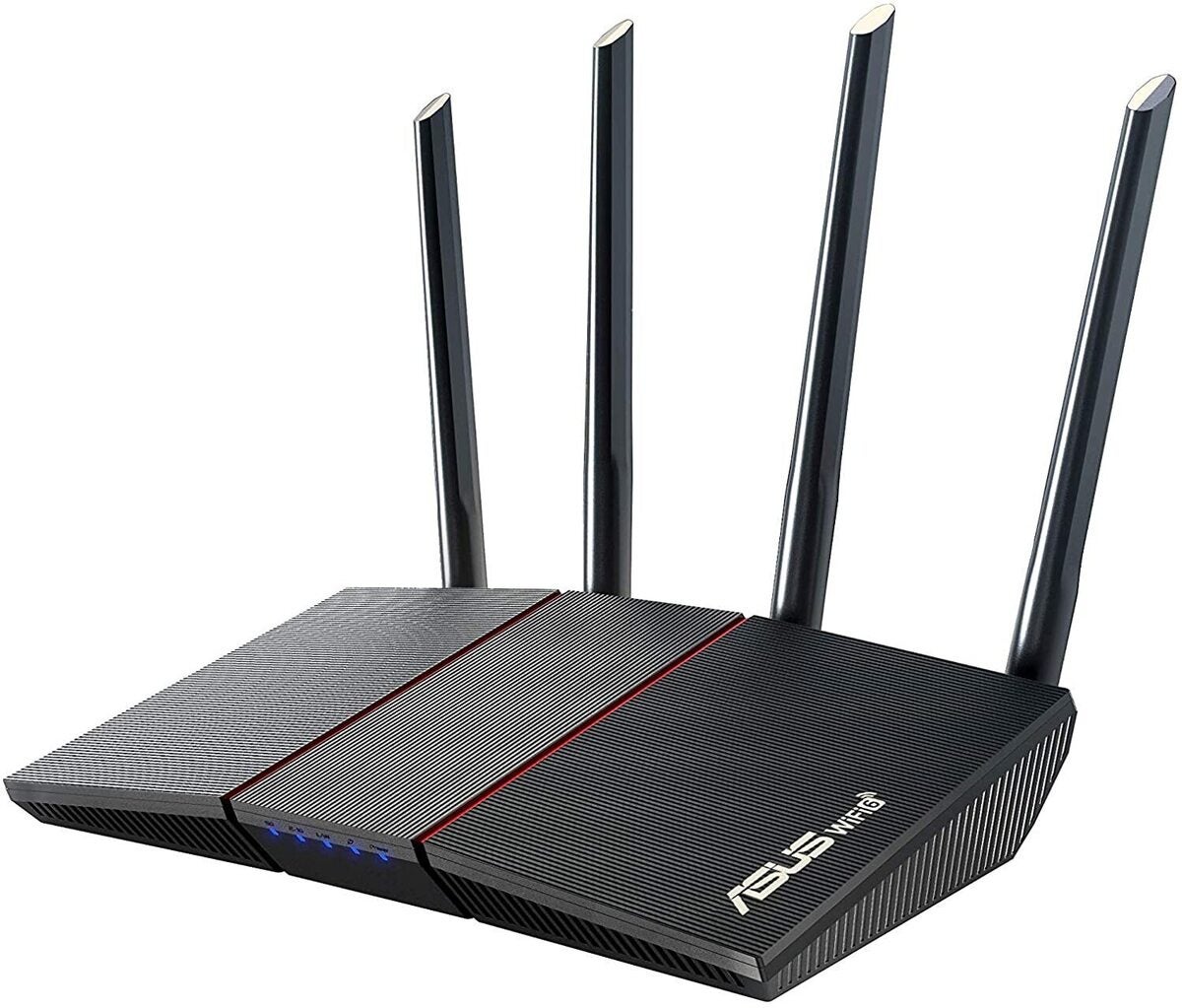 Asus
AsusThe Asus AX1800 features Wi-Fi 6, MU-MIMO for handling multiple devices on the network, and four gigabit LAN ports for wired connections.
Wired vs. wireless
In most cases, a wired connection is the way to go for speed and reliabilityand thats especially important when it comes to gaming. Wireless is still great and super convenient, but it has weaknesses that a direct, wired connection to the router doesnt. That said, gaming over Wi-Fi isnt out of the question. Both connection types have their perks and limitations that will influence what works best for your needs.
Wired
 Cmpl.com
Cmpl.comA Cat5e cable can connect any device with an RJ45 port directly to your router.
Generally speaking, a wired connection between a router and other devices is done by an ethernet or network cable. Without going too deep into the designs and specifications of cables, youll likely want a CAT5e, CAT6, or CAT6a cable with RJ45 plug ends for your wired network cables. CAT5e, CAT6 and CAT6a cables are certified to support up to 1GB connections for up to 100 meters (about 328 feet) of length. CAT6 and CAT6a cables support up to 10GB connections for about half that distance, at about 55 meters. If your wires end up needing to be longer, you may need additional hardware to boost the signal along the way, or accept the potential drop in speed.
In an ideal world, your home is wired up with high-capacity cables and ethernet RJ45 jacks throughout your home. For most homes new and old, though, thats not the case. A more typical scenario is that youll have your desktop computer close enough to where your router or modem resides, so you can wire them up behind a desk or under a table without running cord across the floor. Additional devices will tend to then be wireless to avoid the mess of running cables through the house.
Wireless
 Kevin Casper/IDG
Kevin Casper/IDGWireless network connectivity has come a very long way in a relatively short period of time. Modern wireless standards are already supporting more than gigabit throughput with 802.11ac and 802.11ax pushing up to 3.5Gbps and 9.6Gbps, respectively. For comparison, the global average internet speed is, according to Speedtest, about 107Mbps, meaning that 802.11ac connection can theoretically handle over 30x that capacity. If you are using a wireless router that only supports 802.11 A,B, G, or N, you might be due for an upgrade.
It may be tough to wire up devices in multiple rooms, thanks to all the walls separating them. Wireless connections also deal with wall-related problems. A wireless router has to wrestle with interference from physical objects and other Wi-Fi signals, as well as physics. Generally, the further you are from your wireless router, the worse your connection will be, and youll want your router placed as centrally as possible in your home.
If youre setting up a wireless network in a large space with many rooms, you may want to look into mesh network solutions, such as Netgears Orbi Home WiFi System.
Wireless settings to tweak
You can improve things even more by diving into your routers advanced settings and making a few changes.
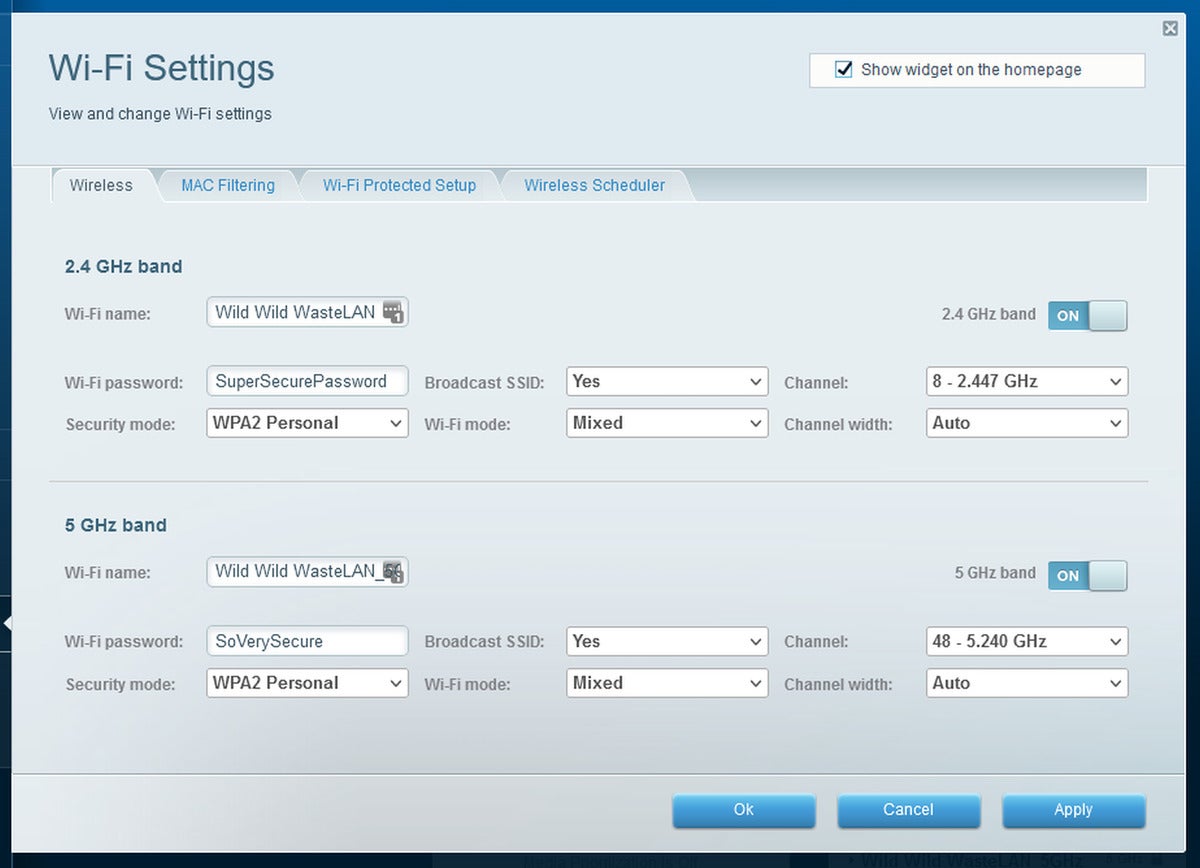
Switching your router to a less-congested Wi-Fi band can help reduce slowdowns. Consider using the 5GHz connection band instead of the typical 2.4GHz band (as long as your device is close enough to the router). You can also set your Wi-Fi connection to use an uncommon wireless channel for your location to help reduce interference. That requires the help of third-party software that scans your network, however. This guide can help.
The way to change your channel and bandwidth settings varies by router manufacturersomething thats true for every tip herebut you can either try visiting 192.168.1.1 in your web browser or viewing your manufacturers support pages. Here are some forAsus,TP-Link,Netgear, andLinksys.
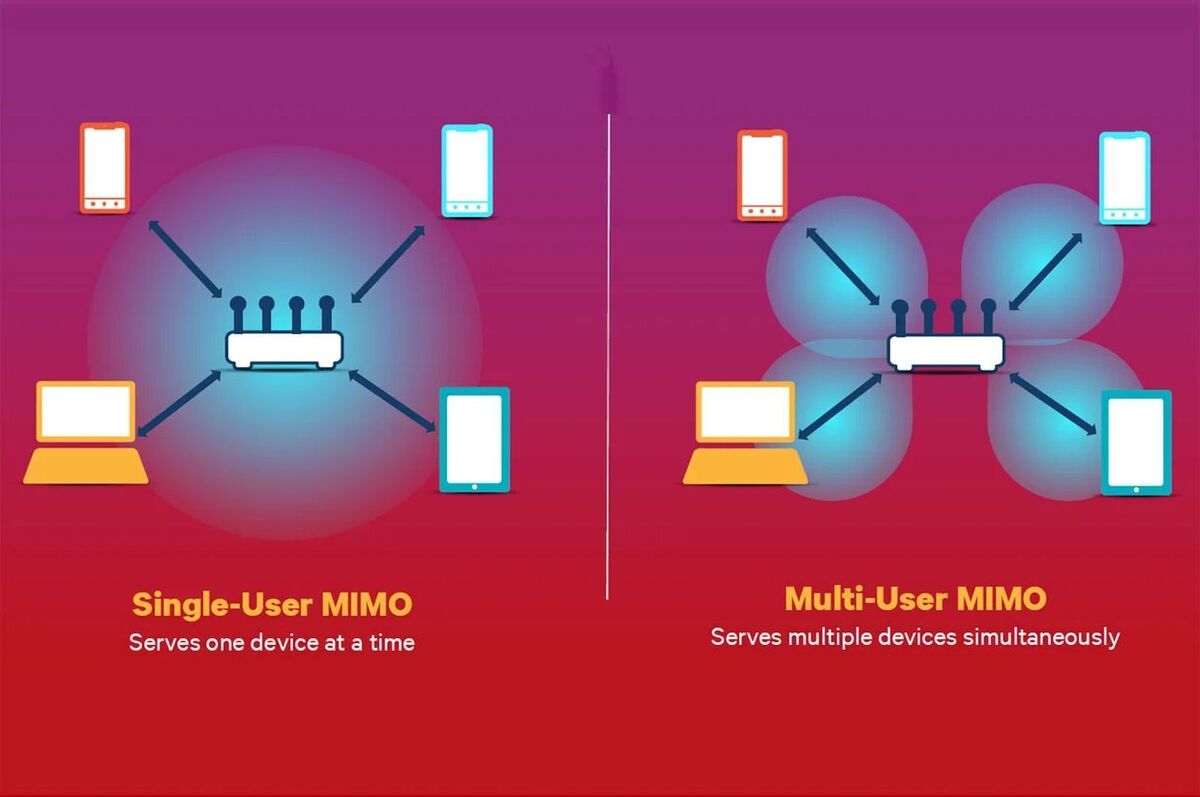 Qualcomm
QualcommAdditionally, if your router supports MU-MIMO, its worth ensuring that its active to reduce the chance of overloading the network with wireless traffic. Multi-User MIMO lets your router talk to several connected devices simultaneously, rather than each device in turn. Flipping it on (if supported) not only makes your Wi-Fi speeds faster, it can let you connect more devices to your network.
Our MU-MIMO explainer from when the technology debuted goes into much more depth if youre interested in hearing more. If youre not, just turn it on!
QoS (Quality of Service)
QoS, or Quality of Service, is the terminology used to describe what is effectively a traffic controller for your network. Basically, all of the data being transferred through your network is handled in packets, which are groups of information that are being downloaded and uploaded to/from devices on your network. Different devices and software will use different amounts, sizes, and frequencies of data packets for whatever they need to do.
Watching your favorite Twitch channel in high-quality tends to need a continuous flow of big packets going to the device youre viewing on. Gaming, on the other hand, tends to be more sporadic with smaller packets going to and from the device youre playing on. If your network is dealing with both, its going to need to direct all of those packets to and from the correct place. QoS settings will let you tell the router how to do that, and what takes precedence.
If gaming is your top priority, many routers provide various types of QoS control settings, allowing you to prioritize a specific device on the network (like your gaming PC) and prioritize what it can detect as certain types of data packets (like your games). By setting your gaming PC and its games to a higher priority than other data packets, the router will then try to ensure your gaming data gets handled correctly, and will drop the packets of other types if the network gets clogged up with too much traffic at once.
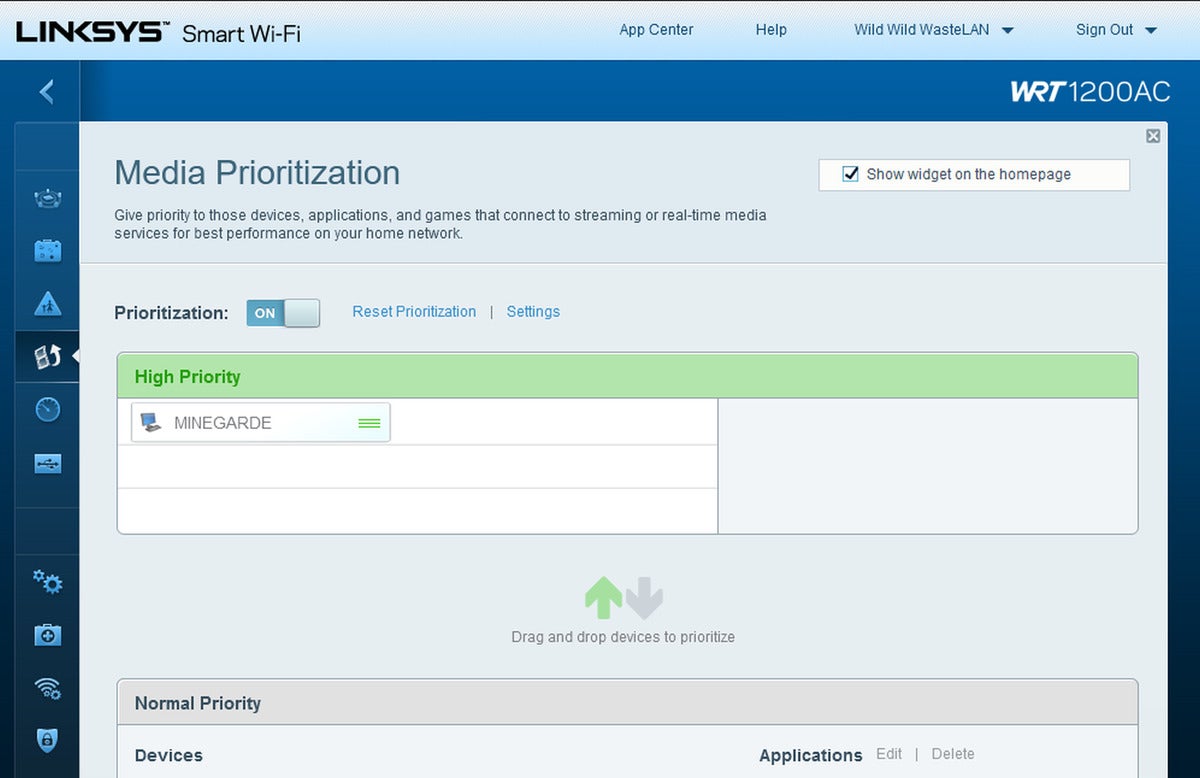 Kevin Casper/IDG
Kevin Casper/IDGNot all router settings are the same, though. You may find QoS options hidden or described as something else. You might need to dig into Advanced Options, or look for something labeled Media Prioritization in order to get the QoS options (as shown above).
Additionally, some routers offer Guest Networks, which are typically a lower-priority network connection that guests can connect to and use your internet connection, but their data packets can take a backseat to your other devices if the traffic gets to be too much.
UPnP, ports, and firewalls
Generally speaking, adjusting more granular options isnt as common an issue as it used to be. With games simplifying their connection needs, and better communication between routers and devices, the idea of port forwarding or directly managing the port connections for your network is less relevant. Most home routers will come with a setting called Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) active, which allows your devices to coordinate with the router on these kinds of things.
However, some of you may need to tweak your managed network settings and open up some ports for your games, especially if UPnP isnt an option. Its rare though, and you shouldnt take these steps unless youre having specific connectivity issues with your games.
 Greeek / Bortania / Getty Images
Greeek / Bortania / Getty ImagesPorts are part of whats known as the transport layer in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model of network communication, and you may have seen them described as TCP or UDP connections. If an IP address is like a postal address for a device on a network, the port numbers are like street names or numbers to let your router know where that traffic needs to go and will be coming from. For example, secure web traffic for a site starting with HTTPS:// will be coming through on Port 443. Some games do provide information about what ports they use, and if youre looking for the best performance, youcould ensure those ports are open on your network.
We should note that open ports on a network can be considered a security risk. One of the easiest ways to help secure your network is by blocking unused ports with your firewall. Thus, if youre setting rules to keep a specific port open, youre potentially keeping a hole open in that firewall and may find yourself in the middle of the endless battle between convenience and security.
Again: Dont mess with these settings unless you have to. Yes, opening ports and tinkering with uPnP used to be a frustrating necessity in the early days of online gaming, but those days are over in the vast majority of modern home networks.