Exploring Haptic Technology How Tech Gear is Creating Realistic Touch Sensations

Hands-free tech adds realistic sense of touch in extended reality
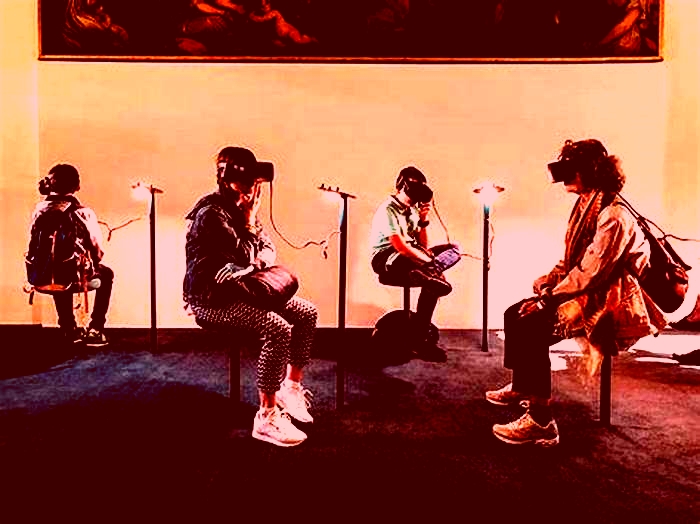
With an eye toward a not-so-distant future where some people spend most or all of their working hours in extended reality, researchers from Rice University, Baylor College of Medicine and Meta Reality Labs have found a hands-free way to deliver believable tactile experiences in virtual environments.
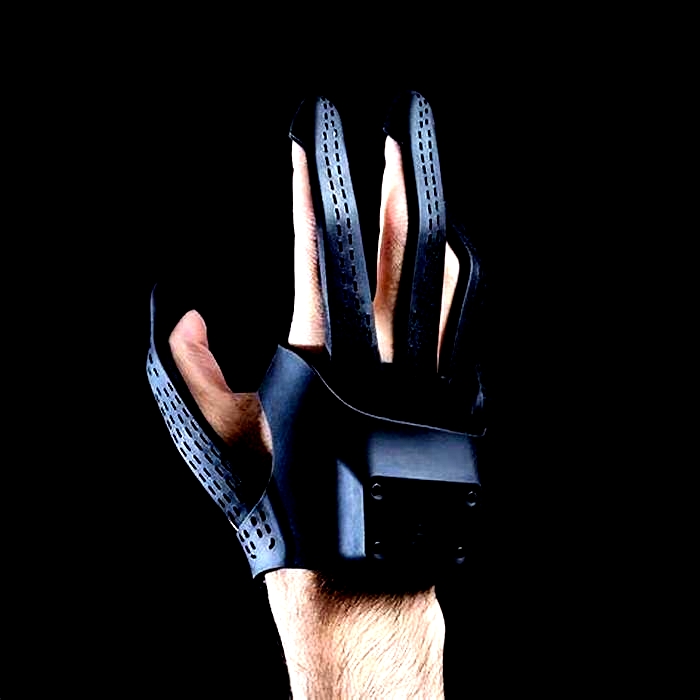
Users in virtual reality (VR) have typically needed hand-held or hand-worn devices like haptic controllers or gloves to experience tactile sensations of touch. The new "multisensory pseudo-haptic" technology, which is described in an open-access study published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems, uses a combination of visual feedback from a VR headset and tactile sensations from a mechanical bracelet that squeezes and vibrates the wrist.
"Wearable technology designers want to deliver virtual experiences that are more realistic, and for haptics, they've largely tried to do that by recreating the forces we feel at our fingertips when we manipulate objects," said study co-author Marcia O'Malley, Rice's Thomas Michael Panos Family Professor in Mechanical Engineering. "That's why today's wearable haptic technologies are often bulky and encumber the hands."
O'Malley said that's a problem going forward because comfort will become increasingly important as people spend more time in virtual environments.
"For long-term wear, our team wanted to develop a new paradigm," said O'Malley, who directs Rice's Mechatronics and Haptic Interfaces Laboratory. "Providing believable haptic feedback at the wrist keeps the hands and fingers free, enabling 'all-day' wear, like the smart watches we are already accustomed to."
Haptic refers to the sense of touch. It includes both tactile sensations conveyed through skin and kinesthetic sensations from muscles and tendons. Our brains use kinesthetic feedback to continually sense the relative positions and movements of our bodies without conscious effort. Pseudo-haptics are haptic illusions, simulated experiences that are created by exploiting how the brain receives, processes and responds to tactile and kinesthetic input.
"Pseudo-haptics aren't new," O'Malley said. "Visual and spatial illusions have been studied and used for more than 20 years. For example, as you move your hand, the brain has a kinesthetic sense of where it should be, and if your eye sees the hand in another place, your brain automatically takes note. By intentionally creating those discrepancies, it's possible to create a haptic illusion that your brain interprets as, 'My hand has run into an object'."
"What is most interesting about pseudo-haptics is that you can create these sensations without hardware encumbering the hands," she said.
While designers of virtual environments have used pseudo-haptic illusions for years, the question driving the new research was: Can visually driven pseudo-haptic illusions be made to appear more realistic if they are reinforced with coordinated, hands-free tactile sensations at the wrist?
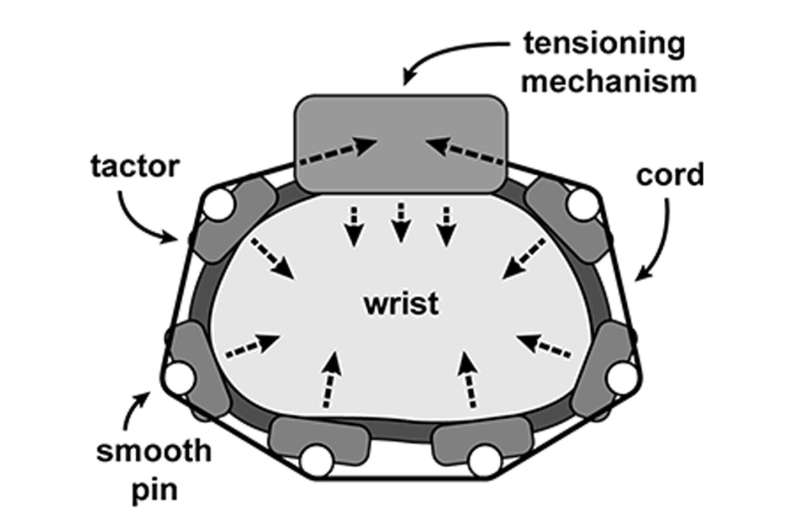
Evan Pezent, a former student of O'Malley's and now a research scientist at Meta Reality Labs in Redmond, Washington, worked with O'Malley and colleagues to design and conduct experiments in which pseudo-haptic visual cues were augmented with coordinated tactile sensations from Tasbi, a mechanized bracelet Meta had previously invented.
Tasbi has a motorized cord that can tighten and squeeze the wrist, as well as a half-dozen small vibrating motorsthe same components that deliver silent alerts on mobile phoneswhich are arrayed around the top, bottom and sides of the wrist. When and how much these vibrate and when and how tightly the bracelet squeezes can be coordinated, both with one another and with a user's movements in virtual reality.
In initial experiments, O'Malley and colleagues had users press virtual buttons that were programmed to simulate varying degrees of stiffness. The research showed volunteers were able to sense varying degrees of stiffness in each of four virtual buttons. To further demonstrate the range of physical interactions the system could simulate, the team then incorporated it into nine other common types of virtual interactions, including pulling a switch, rotating a dial, and grasping and squeezing an object.
"Keeping the hands free while combining haptic feedback at the wrist with visual pseudo-haptics is an exciting new approach to designing compelling user experiences in VR," O'Malley said. "Here we explored user perception of object stiffness, but Evan has demonstrated a wide range of haptic experiences that we can achieve with this approach, including bimanual interactions like shooting a bow and arrow, or perceiving an object's mass and inertia."
Study co-authors include Alix Macklin of Rice, Jeffrey Yau of Baylor and Nicholas Colonnese of Meta.
More information:Evan Pezent et al, Multisensory PseudoHaptics for Rendering Manual Interactions with Virtual Objects, Advanced Intelligent Systems (2023). DOI: 10.1002/aisy.202200303
Citation: Hands-free tech adds realistic sense of touch in extended reality (2023, February 22) retrieved 14 April 2024 from https://techxplore.com/news/2023-02-hands-free-tech-realistic-reality.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Exploring Haptic Feedback on Xbox Series X Controller
Haptic Feedback on Xbox Series X Controller: The Xbox Series X is the latest gaming console from Microsoft that promises to deliver an immersive gaming experience with its advanced features. One of the most notable features of the Xbox Series X is its haptic feedback technology, which provides users with a more tactile and realistic gaming experience. In this article, we will explore haptic feedback on Xbox Series X and how it enhances the overall gaming experience.
Haptic feedback is a technology that provides users with tactile feedback through vibrations and other physical sensations. The Xbox Series X controller features haptic feedback, which enhances the tactile sensations players experience during gameplay. This technology provides a more immersive feel compared to previous Xbox controllers, and it allows players to feel the game in a more realistic way. While the haptic capabilities of the Xbox Series X controller are not as advanced as those found in the PS5 DualSense controller, it still provides a significant improvement over previous Xbox controllers.
Overview of Haptic Feedback on Xbox Series X Controller

The Xbox Series X controller features haptic feedback, which enhances the tactile sensations that players experience during gameplay. This technology provides a more immersive feel compared to previous Xbox controllers. However, its worth noting that its haptic capabilities are not as advanced as those found in the PS5 DualSense controller.
Haptic feedback on the Xbox Series X controller is designed to provide users with a more realistic and engaging gaming experience. The technology uses vibrations to simulate the sensation of touch, allowing players to feel the impact of their actions in the game. For example, if a player is driving a car in a racing game and hits a wall, they will feel a jolt in the controller that simulates the impact.
The Xbox Series X controller also features adaptive triggers that allow for more precise control over in-game actions. These triggers can adjust the tension and resistance of the buttons, providing users with a more realistic experience. For example, if a player is firing a gun in a first-person shooter game, the trigger will provide resistance that simulates the recoil of the weapon.
Overall, the haptic feedback on the Xbox Series X controller is a significant improvement over previous generations of Xbox controllers. While it may not be as advanced as the haptic feedback found on the PS5 DualSense controller, it still provides users with a more immersive gaming experience.
Technological Foundations of Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback is a technology that simulates touch sensations in electronic devices. It is a critical component of modern gaming controllers, including the Xbox Series X controller. Haptic feedback is achieved through the use of tactile actuators and haptic feedback motors.
Tactile Actuators
Tactile actuators are small devices that convert electrical signals into physical motion. They are responsible for creating the tactile sensations that gamers experience when they press buttons or trigger actions on the controller. Tactile actuators are typically made of materials such as piezoelectric ceramics or electroactive polymers. They can be designed to produce a variety of sensations, including vibration, pressure, and texture.
Haptic Feedback Motors
Haptic feedback motors are specialized motors that are used to create more advanced haptic feedback. They are commonly found in high-end gaming controllers, including the Xbox Series X controller. Haptic feedback motors can produce more complex sensations than tactile actuators, such as directional vibrations and pulsing rhythms. They are typically more powerful than tactile actuators and can provide a more immersive gaming experience.
Overall, the technological foundations of haptic feedback are based on the ability to convert electrical signals into physical motion. This technology is critical for creating realistic and immersive gaming experiences. The Xbox Series X controller uses both tactile actuators and haptic feedback motors to provide gamers with a wide range of touch sensations.
Design and Ergonomics of the Xbox Series X Controller
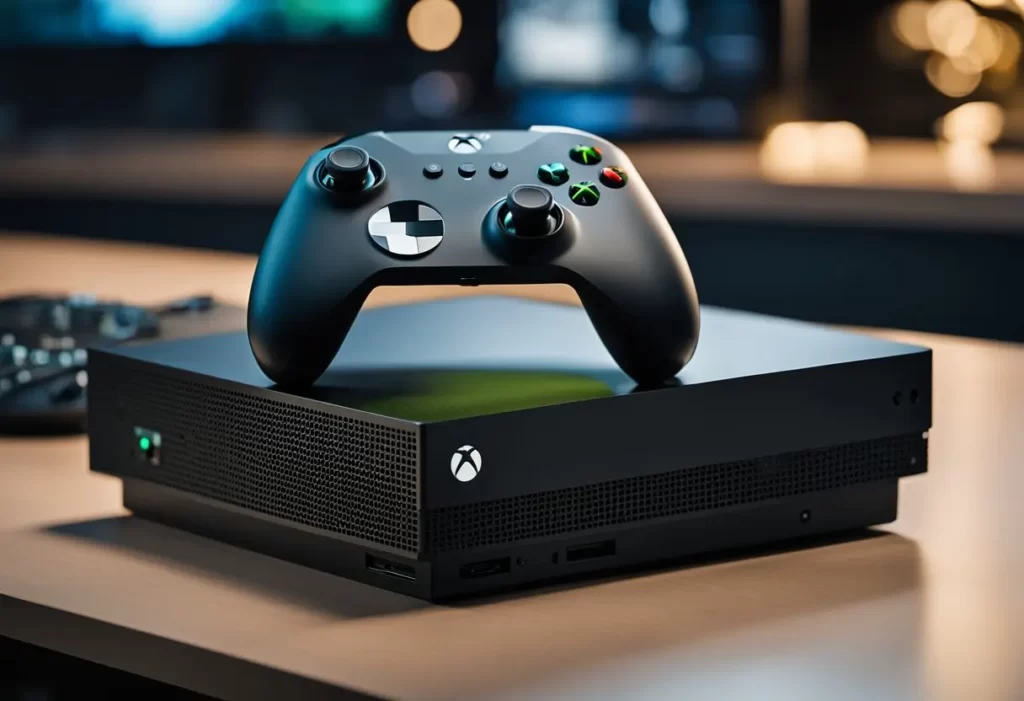

The Xbox Series X controller, designed by Microsoft, has a sleek and ergonomic design that makes it comfortable to hold for long periods. The controllers design is an evolution of the Xbox One controller, with subtle refinements to make it more comfortable and responsive.
Adaptive Triggers
One of the most significant changes to the Xbox Series X controller is the addition of adaptive triggers. These triggers provide varying levels of resistance, making the controller feel more immersive and realistic. This feature allows developers to create games that have a more realistic feel, such as shooting a bow and arrow or driving a car.
Textured Grips
Another significant change to the Xbox Series X controller is the addition of textured grips. The controllers grips have a unique texture that makes it easier to hold, even during intense gaming sessions. The grips also help to prevent the controller from slipping out of the players hands, improving control and accuracy.
Overall, the Xbox Series X controller is a well-designed and ergonomic device that provides a comfortable and immersive gaming experience. With its adaptive triggers and textured grips, the controller is a significant improvement over the Xbox One controller, and it is sure to be a hit with gamers worldwide.
User Experience and Interaction
Immersive Gameplay
One of the most exciting features of the Xbox Series X is the immersive gameplay experience that it provides through haptic feedback. The Xbox Series X controller has four vibration motors a small one behind each trigger and a larger one in each grip. This provides precise haptic feedback to the fingertips and a sense of in-game directionality and depth. The haptic feedback creates rich, immersive experiences for players, making them feel like they are part of the game.
The haptic feedback on Xbox Series X is not just limited to vibrations. Games can also use haptic feedback to provide a variety of sensations, such as the feeling of raindrops hitting the controller or the sensation of a car engine revving up. This makes the gameplay experience more immersive and engaging.
Accessibility Features
Haptic feedback is not just a fun feature for gamers, it also has practical applications for accessibility. The Xbox Series X controllers haptic feedback can be used to provide tactile feedback for players with visual impairments. For example, haptic feedback can be used to indicate the direction of an enemys attack or the location of an objective. This makes the game more accessible to players with disabilities and provides a more inclusive gaming experience.
In addition to haptic feedback, the Xbox Series X controller also has other accessibility features, such as a built-in speech-to-text function and customizable button mapping. These features make the Xbox Series X more accessible to a wider range of gamers, regardless of their abilities.
Overall, the haptic feedback and accessibility features on the Xbox Series X provide a more immersive and inclusive gaming experience for players.
Game Development and Haptic Integration

Developer Tools and APIs
Developers can integrate haptic feedback into their games on Xbox Series X using Microsofts Game Development Kit (GDK). The GDK provides access to the Xbox Series X controllers haptic features, allowing game developers to create more immersive gameplay experiences.
In addition to the GDK, Xbox Series X developers can also use the Xbox Accessibility Guidelines to ensure their games are accessible to players with disabilities. The guidelines include recommendations for haptic feedback, such as using vibration to indicate important events or actions in the game.
Case Studies of Haptic Implementation
Several games have already implemented haptic feedback on the Xbox Series X controller. For example, in the game Forza Horizon 5, players can feel the rumble of their cars engine and the impact of collisions through the controllers haptic feedback. In Halo Infinite, the controllers triggers provide resistance when firing certain weapons, adding a new level of immersion to the gameplay.
Another example of haptic integration can be seen in the game Psychonauts 2, where players can feel the different textures of the games environments through the controllers haptic feedback. Sand feels gritty, while metal feels smooth, adding a new layer of realism to the game.
Overall, the Xbox Series Xs haptic feedback capabilities provide game developers with a new tool to create more immersive and engaging gameplay experiences. By using the GDK and Xbox Accessibility Guidelines, developers can ensure that their games are accessible to all players, including those with disabilities.
Comparative Analysis
Xbox Series X vs. PlayStation 5 Haptics
The Xbox Series X controller features haptic feedback that enhances the tactile sensations players experience during gameplay. While it provides a more immersive feel compared to previous Xbox controllers, its worth noting that its haptic capabilities are not as advanced as those found in the PS5 DualSense controller [1]. The PS5 DualSense controller features new haptic feedback motors and adaptive triggers, which provide more immersive and nuanced feedback to players [2].
The Xbox Series X controllers haptic feedback is more subtle and less pronounced than that of the PS5 DualSense controller. However, its still an improvement over previous Xbox controllers, and provides a more immersive gaming experience overall.
Previous Generation Xbox Controllers
Compared to previous generation Xbox controllers, the Xbox Series X controllers haptic feedback is a significant improvement. The Xbox Ones wireless controller, for example, features four vibration motors a small one behind each trigger that adds precise haptic feedback to the fingertips, and a larger one in each grip for large-scale rumbles [3]. The Xbox Series X controller builds on this foundation and provides more nuanced haptic feedback that enhances the overall gaming experience.
Overall, the Xbox Series X controllers haptic feedback is a significant improvement over previous generation Xbox controllers, but falls short of the more advanced haptic capabilities found in the PS5 DualSense controller.
Future of Haptic Technology in Gaming Consoles
Haptic feedback technology has come a long way in the gaming industry, and it is expected to continue evolving in the future. The Xbox Series X has already set the bar high with its advanced haptic feedback features, such as the VCA haptics that double as speakers, and the Sebile controller that includes an accelerometer which should let you merely lift it to wake the gamepad.
As gaming consoles continue to become more powerful, the technology behind haptic feedback is expected to advance as well. It is likely that future gaming controllers will feature more advanced haptic feedback that can simulate a wider variety of sensations, such as different types of textures and temperatures.
Additionally, haptic feedback technology may also be integrated into other aspects of gaming, such as virtual reality. It is possible that future VR headsets will include haptic feedback features that can simulate the sensation of touch and movement, making the gaming experience even more immersive.
Overall, the future of haptic technology in gaming consoles is bright, and it is likely that we will see even more advanced features in the coming years. As developers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, we can expect to see haptic feedback become an even more integral part of the gaming experience.
You might also like