Exploring Biometric Authentication Fingerprint Scanners Facial Recognition and Beyond

Facial Recognition vs. Fingerprint Identification: Which Should You Use?
Facial recognition vs. fingerprint identification: is one better than the other? Security teams today are shifting to biometrics, prompting an assessment of whether fingerprinting remains viable in a digital context or whether selfies now offer a better option.
Here well cover what you need to know to make an informed assessment. First, well look at these two technologies individually and examine their respective pros and cons. Then well compare facial recognition vs. fingerprint accuracy and reliability to help you evaluate how these two biometrics solutions fit your current and future security needs.
Facial Recognition vs. Fingerprint Recognition: What Are They?
Lets start by looking at fingerprint recognition and facial recognition separately. We will highlight the pros and cons of each method, providing a basis for comparison.
What Is Fingerprint Recognition?
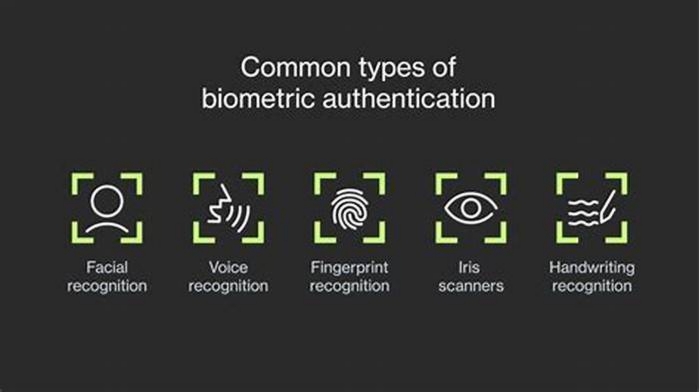
Fingerprint recognition is a method ofbiometric authenticationthat confirms an individuals identity by using an image of their fingertips. Fingerprinting methods of identification rely on the fact that each persons fingertips are marked by unique patterns known as friction ridges. No two people have the same fingerprint patterns, allowing fingerprints to be used as an identification method. If a persons fingerprint is on file, a fingerprint recognition check can be run by software to confirm their identity.
Several methods of fingerprint recognition are in everyday use:
- Optical scanners use a digital image of a fingertip
- Capacitive scanners (Complementary Metal-oxide-semiconductor or CMOS scanners) use electrical patterns on a persons skin to extract fingerprint images
- Ultrasonic fingertip scanners use sound waves to penetrate the outer layer of the skin and create images
- Thermal scanners use heat differences between fingertip ridges and surrounding valleys to create images
A typical fingerprint recognition application uses a smartphone camera to take an optical image. Standalone scanners fixed to a wall or door are used for security checks in buildings.
Fingerprint Recognition Pros and Cons
Fingerprints offer several advantages to security teams:
- Fingerprints vary from one individual to another, serving as a unique identifier
- A persons fingerprints dont change significantly over time
- Fingerprints can be taken and analyzed to a high degree of accuracy
- Fingerprinting is easy to apply to smartphones for remote verification
- Fingerprint recognition technology is inexpensive
On the other hand, fingerprinting has some drawbacks:
- Criminals can copy fingerprints using means such as photographs of fingertips or 3D molds of fingertips
- Fingerprinting requires physical contact with a scanner, which can spread germs
To address fingerprint impersonation attempts, smartphone fingerprint recognition scanners have shifted from optical scanners, which can be fooled by photographs of fingerprints, to capacitive scanners, which can differentiate 2D from 3D images. An enterprising criminal or spy can still create a 3D mold, but this takes more work and is impractical to do at scale.
What Is Facial Recognition?
Facial recognition authenticates an individuals identity by comparing a live image of their face with a photo of their face on file. A facial recognition software system analyzes the live image and checks it against the stored image to verify a match.
Several methods of facial recognition are used:
- An algorithm analyzes spatial relationships between facial landmarks, such as the distance between a persons eyes
- Capturing and analyzing 3D information about a persons face using 3D sensors or combinations of 2D camera images taken at slightly different angles
- Face ID, a facial recognition system developed by Apple, analyzes an image taken on a smartphone or tablet camera created by illuminating the subjects face in infrared light
- Enhancing low-resolution images of individuals photographed at a distance for comparison with higher-resolution photos
- Analyzing thermal images of faces, which factor out low-temperature accessories such as makeup, glasses, and hats
Facial recognition is widely used as a security check for smartphone access. It also has been used as a social media account authentication method. Other applications include robot vision and healthcare identity confirmation before surgery.
Facial Recognition Pros and Cons
Facial recognition has several points in its favor:
- Its easy for smartphone users
- It can be used as a method ofidentity proofingfor remoteonline authentication
- Its inexpensive
- It can be applied without contact
- It doesnt spread germs through contact
- It can be used to identify faces in crowds
On the other hand, facial recognition has some disadvantages:
- Facial recognition software works better at frontal and near-frontal angles but loses accuracy as the camera moves toward a profile shot
- Changes in facial expression or style changes, such as beards and glasses, can confuse facial recognition systems.
- Lighting conditions can affect facial recognition results
- Photos can be used for facial recognition without the users consent, creating privacy concerns
- Criminals can attempt to bypass facial recognition systems using means such as photos of faces, 3D models, or deepfake videos
- Multiple accidental triggering of facial recognition authentication can lock a smartphone user out of their device
Facial recognition developers are continually upgrading technology to address some of these issues. Current facial recognition systems use multiple camera angles and can distinguish 2D photo impersonations from 3D live photos. Subjects can be recognized even when wearing accessories, makeup, or facial hair. Users can adjust accessibility settings on smartphones to avoid accidental triggering of facial recognition checks.
Facial Recognition vs. Fingerprint Accuracy
Fingerprint recognition can confirm individual identity more accurately than facial recognition systems. However, this may change as facial recognition systems become increasingly integrated with iris recognition, another biometric authentication method with high accuracy.
Iris recognition detects patterns in an individuals eyes that are as unique as fingerprints and can be captured from a distance. Iris recognition can be built into facial recognition systems, joining the accuracy of fingerprints to the convenience and hygiene of contactless authentication. However, iris recognition still has some limitations, such as requiring special cameras and taking a long time to scan, so fingerprint recognition remains the most accurate biometric authentication method.
Face ID vs. Touch ID: Which Is Most Reliable?
Touch ID is currently more reliable than Face ID for some of the reasons which have been touched upon:
- Fingerprints are less subject to change than facial appearance
- Fingerprint recognition doesnt depend on a specific camera angle
- Fingerprint patterns are more unique than facial patterns
However, future developments such as iris recognition integration may improve the reliability of Face ID and other facial recognition systems. In addition, Face ID currently enjoys advantages such as ease of use, contactless data capture, and hygiene. Both types of technology retain a role in biometric authentication.
Prepare for the Future of Face ID and Touch ID Biometrics with Incode
The constantly changing state of biometrics technology makes it likely that fingerprint and facial recognition will both remain essential security tools in the near future. The globalfingerprint sensor marketis on track to achieve an annual compound growth rate of 14.5% between 2020 and 2027, while the globalfacial recognition marketis positioned to grow at a comparable rate of 15.4% between 2021 and 2028. To keep up with biometrics trends and technology changes on the horizon, you need a security technology platform that stays up-to-date.
TheIncode Omni platformis constantly adapting to the latest security technology. Powered by cutting-edge artificial intelligence, Omni features fingerprint and facial recognition as part of a comprehensive authentication tool that makes it quick and easy for your customers to swiftly and securely confirm their identities.Contactus todayto request a demo and see how we can help you provide a frictionless security experience to your customers.
Facial Recognition for Authentication: How It Works & Why It Matters
The quest for secure yet user-friendly ways to access online services, physical locations, and digital resources has led to the rise of facial recognition authentication. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of facial recognition, exploring how it works, its advantages, and its diverse applications across various sectors.
One of Biometrics Methods: Facial Recognition Authentication
Facial recognition authentication, also known as facial biometric authentication, is a cutting-edge technology that leverages an individual's facial features to verify their identity. In a landscape where digital security is a top priority, this method has gained prominence and is used in a variety of contexts, from unlocking personal devices to securing critical infrastructure.
The use of facial recognition is so widespread that it has become second nature for many of us. Unlocking a smartphone with a glance or accessing online accounts using facial recognition has become a daily routine. In fact, over 70% of governments worldwide have embraced facial recognition technology, and approximately 40% have used it to combat the spread of COVID-19.
When Apple introduced Face ID in 2017 with the iPhone X, it marked a significant milestone in the adoption of facial recognition for authentication. This technology revolutionized the way we secure our devices, offering a seamless and secure experience. Today, most modern smartphones and tablets feature some form of facial recognition, making it a common choice for biometric authentication.
Developers have harnessed facial recognition authentication to enhance both the security and user experience of their applications and websites. But how does this technology work, and what makes it so attractive?
Facial Biometrics Authentication: How It Works
Facial recognition authentication consists of two key processes: enrollment and authentication. Let's break down these processes to understand how the technology operates.
Enrollment
Capturing facial data: The enrollment process begins with capturing a detailed scan of an individual's facial features. This initial scan is typically performed by the camera hardware on the user's device, ensuring that the biometric data remains secure. The scans create a 3D model of the user's facial anatomy through machine learning, ensuring precision and reliability.
Creating a biometric template: The captured facial data is transformed into a unique biometric template, often referred to as a "faceprint." This template represents the individual's facial features, including distances between key landmarks such as the eyes and the forehead-to-chin measurements. Each person's faceprint is distinct and serves as their digital identity.
Authentication
Face matching algorithms: When a user attempts to authenticate, the system captures a new face scan. This scan is compared to the stored biometric template. If the system deems the two scans to be an accurate match, access is granted. However, if there is a mismatch, the user may be prompted for a re-attempt or asked for an alternative form of identification.
Verifying the user's identity: The accuracy of facial recognition technology has improved significantly in recent years, with leading algorithms achieving near-human precision. Advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence have addressed challenges related to varying lighting conditions, angles, and demographic biases, enhancing recognition rates across diverse populations.
It's essential to note that the success of facial recognition authentication depends on the hardware, software, and user device permissions. This integration ensures a seamless and secure experience.
Advantages of Facial Recognition Authentication
Facial recognition authentication offers a range of benefits, making it a compelling choice for a variety of applications. Let's explore these advantages in more detail.
Security and Accuracy
Facial recognition provides a high level of security. Each person's face is unique, making it challenging for unauthorized individuals to gain access. In fact, with technologies like Apple's Face ID, the likelihood of a random person's face unlocking another user's account is less than one in a million. Moreover, most device-based facial recognition technologies support additional security measures, such as passkeys and WebAuthn, further fortifying the authentication process.
User Convenience
One of the most prominent advantages of facial recognition is the unparalleled convenience it offers to users. Authentication becomes a seamless process, requiring nothing more than a quick glance. Users no longer need to remember and input passwords or carry physical tokens, enhancing overall satisfaction and encouraging widespread adoption.
Liveness Detection
To further enhance security, many facial recognition systems incorporate liveness detection. Users may be prompted to perform specific actions, such as nodding or smiling during authentication, ensuring that the system interacts with a live individual rather than a static image. This additional layer of security minimizes the risk of fraudulent access attempts.
Efficiency and Speed
Facial recognition authentication is exceptionally efficient and fast. Users can gain access with a brief look, saving valuable time compared to traditional authentication methods. This speed is particularly advantageous in time-sensitive environments or high-traffic areas where quick and secure access is essential.
Contactless Interactions
In a world increasingly concerned about hygiene and safety, facial recognition offers a contactless authentication method. This minimizes physical touch, making it particularly valuable in public spaces, healthcare settings, and other environments where reducing germ transmission is a priority.
Facial Recognition Applications
Facial recognition technology finds applications across various industries and sectors. Here are some common use cases:
Access Control and Security
- Building Entry: Offices, hotels, and residential complexes grant authorized individuals access without the need for keys or access cards.
- Airport Security: Airports use facial recognition to match travelers' faces with passport photos during check-in and boarding, ensuring accurate identity verification.
Financial Services
- Mobile Banking: Banks provide secure and convenient access to mobile banking apps, allowing users to check balances, transfer funds, and make payments.
- ATM Withdrawals: Facial recognition at ATMs reduces the risk of card theft and PIN-based fraud while enabling secure fund withdrawals.
Retail and Ecommerce
- Personalized Shopping: Retailers identify and greet loyal customers, offering personalized recommendations and discounts based on previous purchases.
- Online Authentication: Facial recognition software allows users to securely and conveniently log in to their online accounts by analyzing their unique facial features for seamless authentication.
Healthcare
- Patient Identification: Hospitals and clinics accurately match patients with their medical records, reducing the risk of medical errors and ensuring proper care delivery.
- Telemedicine Authentication: Facial recognition confirms the identity of both patients and healthcare professionals during virtual consultations.
Education
- Campus Security: Educational institutions enhance campus security by using facial recognition to identify authorized personnel and visitors, improving overall safety.
- Attendance Tracking: Facial recognition streamlines attendance tracking in schools and universities, automating the process and reducing administrative workload.
Law Enforcement and Public Safety
- Criminal Identification: Law enforcement agencies compare images of suspects with databases of known criminals, aiding in criminal identification and investigation.
- Finding Missing People: Face recognition CCTV systems enable police to swiftly locate missing individuals by matching reference photos with past video appearances, enabling real-time alerts for accurate recovery.
Upgrade Your Security with Passwordless Authentication!
Are you sure relying solely on OTPs enough to meet your security requirements? It's time to explore a more secure and cost-effective solution Fazpass Seamless Authentication. With a proven track record since 2016, Fazpass guarantees 99.9% uptime and remains committed to continuous innovation to cater to all your authentication needs.
Manage all your OTPs effortlessly within a single platform, delivering a seamless user experience without straining your budget. Trusted by startups and unicorns alike, Fazpass aligns with FIDO standards to ensure top-tier security and your peace of mind. Elevate your security and simplify your authentication processes with Fazpass today!
TRY SEAMLEASS AUTHENTICATION NOW!