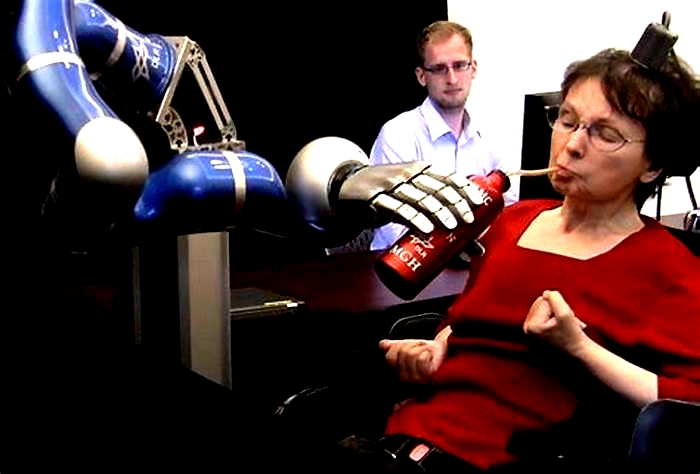
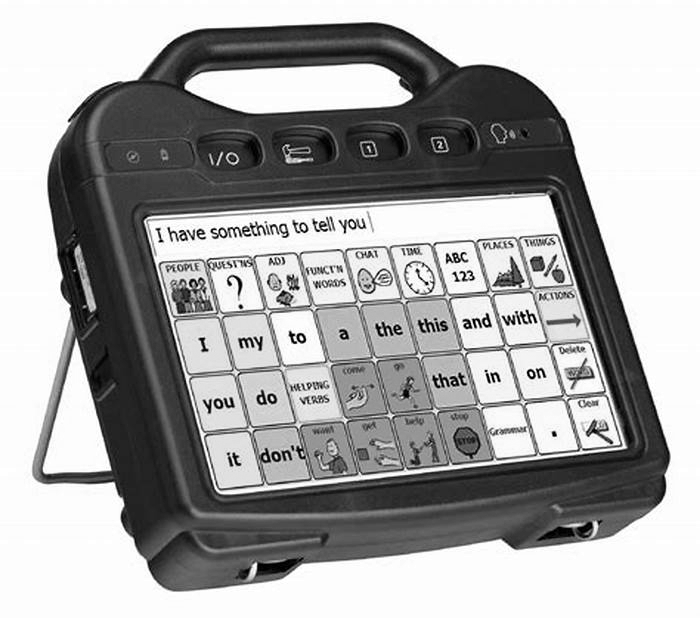
Brain Computer Interfaces for Communication Utilizing Thought Patterns to Control Communication Devices
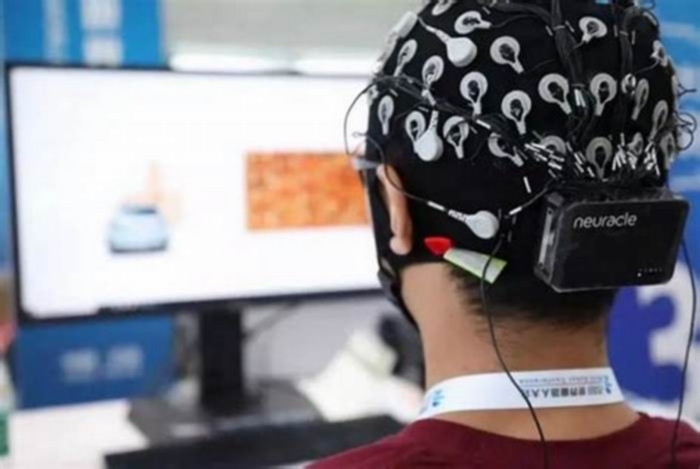

Braincomputer interfaces for communication and rehabilitation
Wyrwicka, W. & Sterman, M. B. Instrumental conditioning of sensorimotor cortex EEG spindles in the waking cat. Physiol. Behav. 3, 703707 (1968).
Article Google Scholar
Kamiya, J. in Altered states of consciousness. (ed Tart, C.) 519529 (New York: Wiley, 1969).
Google Scholar
Fetz, E. E. & Baker, M. A. Operantly conditioned patterns on precentral unit activity and correlated responses in adjacent cells and contralateral muscles. J. Neurophysiol. 36, 179204 (1973).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Vidal, J.-J. Toward direct brain-computer communication. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 2, 157180 (1973). The first paper describing a brain computer interface and the hypothetical learning mechanisms involved.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sterman, M. B., Wyrwicka, W. & Roth, S. Electrophysiological correlates and neural substrates of alimentary behavior in the cat. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 157, 723739 (1969).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sterman, M. & Friar, L. Suppression of seizures in epileptic Following on sensorimotor EEG feedback training. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 33, 8995 (1972).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lubar, J. F. & Shouse, M. N. EEG and behavioral changes in a hyperkinetic child concurrent with training of the sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) - A preliminary report. Biofeedback Self Regul. 1, 293306 (1976).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sterman, M. B. & Macdonald, L. R. Effects of central cortical EEG feedback training on incidence of poorly controlled seizures. Epilepsia 19, 207222 (1978).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Chapin, J. K., Moxon, K. A., Markowitz, R. S. & Nicolelis, M. A. L. Real-time control of a robot arm using simultaneously recorded neurons in the motor cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 664670 (1999).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Donoghue, J. P. Connecting cortex to machines: recent advances in brain interfaces. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 10851088 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Nicolelis, M. A. L. Actions from thoughts. Nature 409, 403407 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Velliste, M., Perel, S., Spalding, M. C., Whitford, A. S. & Schwartz, A. B. Cortical control of a prosthetic arm for self-feeding. Nature 453, 10981101 (2008).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Taylor, D. M., Tillery, S. I. H. & Schwartz, A. B. Direct Cortical Control of 3D Neuroprosthetic Devices. Sci. 296, 18291832 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Santhanam, G., Ryu, S. I., Yu, B. M., Afshar, A. & Shenoy, K. V. A high-performance brain-computer interface. Nature 442, 195198 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wessberg, J. et al. Real-time prediction of hand trajectory by ensembles of cortical neurons in primates. Nature 408, 361365 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Serruya, M. D., Hatsopoulos, N. G., Paninski, L., Fellows, M. R. & Donoghue, J. P. Brain-machine interface: Instant neural control of a movement signal. Nature 416, 141142 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Carmena, J. M. et al. Learning to control a brainmachine interface for reaching and grasping by primates. PLoS Biol. 1, e2 (2003). This paper provides the most advanced and detailed neurophysiological analysis of the neuronal mechanisms behind braincomputer interface control of complex movements.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Hochberg, L. R. et al. Neuronal ensemble control of prosthetic devices by a human with tetraplegia. Nature 442, 164171 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Donoghue, J. P., Nurmikko, A., Black, M. & Hochberg, L. R. Assistive technology and robotic control using motor cortex ensemble-based neural interface systems in humans with tetraplegia. J. Physiol. 579, 603611 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N., Ramos Murguialday, A., Weber, C. & Montoya, P. Chapter 8 neurofeedback and brain-computer Interface: clinical applications. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 86, 107117 (2009).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fuchs, T., Birbaumer, N., Lutzenberger, W., Gruzelier, J. H. & Kaiser, J. Neurofeedback treatment for attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder in children: a comparison with methylphenidate. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 28, 112 (2003).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Monastra, V. J. et al. Electroencephalographic biofeedback in the treatment of attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder. J. Neurother. 9, 534 (2006).
Article Google Scholar
Kotchoubey, B. et al. Modification of slow cortical potentials in patients with refractory epilepsy: a controlled outcome study. Epilepsia 42, 406416 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Gilja, V. et al. Clinical translation of a high-performance neural prosthesis. Nat. Med. 21, 11421145 (2015).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hochberg, L. R. et al. Reach and grasp by people with tetraplegia using a neurally controlled robotic arm. Nature 485, 372375 (2012). The first paper describing multidemensional movement control of an armhand robotic device using an implanted microelectrode array in the primary motor cortex of a paralyzed patient.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jarosiewicz, B. et al. Virtual typing by people with tetraplegia using a stabilized, self-calibrating intracortical brain-computer interface. IEEE BRAIN Gd. Challenges Conf. Washington, DC 7, 111 (2014).
Google Scholar
Pfurtscheller, G., Mller, G. R., Pfurtscheller, J., Gerner, H. J. & Rupp, R. 'Thought ' control of functional electrical stimulation to restore hand grasp in a patient with tetraplegia. Neurosci. Lett. 351, 3336 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Caria, A., Sitaram, R. & Birbaumer, N. Real-time fMRI: a tool for local brain regulation. Neuroscientist. 18, 487501 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chaudhary, U., Birbaumer, N. & Curado, M. R. Brain-machine interface (BMI) in paralysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 58, 913 (2015).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Nijboer, F. et al. An auditory braincomputer interface (BCI). J. Neurosci. Methods 167, 4350 (2008).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chatterjee, A., Aggarwal, V., Ramos, A., Acharya, S. & Thakor, N. V. A brain-computer interface with vibrotactile biofeedback for haptic information. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 4, 112 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Lugo, Z. R. et al. A vibrotactile p300-based brain-computer interface for consciousness detection and communication. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 45, 1421 (2014).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bansal, A. K., Truccolo, W., Vargas-Irwin, C. E. & Donoghue, J. P. Decoding 3D reach and grasp from hybrid signals in motor and premotor cortices: spikes, multiunit activity, and local field potentials. J. Neurophysiol. 107, 13371355 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Flint, R. D., Wright, Z. A., Scheid, M. R. & Slutzky, M. W. Long term, stable brain machine interface performance using local field potentials and multiunit spikes. J. Neural Eng. 10, 056005 (2013).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
So, K., Dangi, S., Orsborn, A. L., Gastpar, M. C. & Carmena, J. M. Subject-specific modulation of local field potential spectral power during brain-machine interface control in primates. J. Neural Eng. 11, 026002 (2014).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mehring, C. et al. Comparing information about arm movement direction in single channels of local and epicortical field potentials from monkey and human motor cortex. J. Physiol. Paris 98, 498506 (2004).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Georgopoulos, A. P., Schwartz, A. B. & Kettner, R. E. Neuronal population coding of movement direction. Science 233, 14161419 (1986).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Georgopoulos, A. P. & Kettner, R. E. & Schwartz, A. B. Primate motor cortex and free arm movements to visual targets in three-dimensional space. II. Coding of the direction of movement by a neuronal population. J. Neurosci. 8, 29282937 (1988).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Serruya, M., Hatsopoulos, N., Paninski, L., Fellows, M. R. & Donoghue, J. P. Brain-machine interface: Instant neural control of a movement signal. Nature 416, 121142 (2002).
Article Google Scholar
Leuthardt, E. C., Schalk, G., Wolpaw, J. R., Ojemann, J. G. & Moran, D. W. A braincomputer interface using electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural Eng. 1, 6371 (2004).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Felton, E. a, Wilson, J. A., Williams, J. C. & Garell, P. C. Electrocorticographically controlled brain-computer interfaces using motor and sensory imagery in patients with temporary subdural electrode implants. Report of four cases. J. Neurosurg. 106, 495500 (2007).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Clancy, K. B., Koralek, A. C., Costa, R. M., Feldman, D. E. & Carmena, J. M. Volitional modulation of optically recorded calcium signals during neuroprosthetic learning. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 807809 (2014).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N., Elbert, T., Canavan, A. & Rockstroh, B. Slow potentials of the cerebral cortex and behavior. Physiol. Rev. 70, 141 (1990).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kubler, A. et al. Brain-computer communication: self regulation of slow cortical potentials for verbal communication. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 82, 15331539 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N., Hinterberger, T., Kbler, A. & Neumann, N. The thought-translation device (TTD): neurobehavioral mechanisms and clinical outcome. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 11, 120123 (2003).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pfurtscheller, G. & Aranibar, A. Evaluation of event-related desynchronization (ERD) preceding and following voluntary self-paced movement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 46, 138146 (1979).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kbler, A. et al. Patients with ALS can use sensorimotor rhythms to operate a brain-computer interface. Neurology 64, 17751777 (2005).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Wolpaw, J. R. et al. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 113, 767791 (2002).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Farwell, L. A. & Donchin, E. Talking off the top of your head: toward a mental prosthesis utilizing event-related brain potentials. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 70, 510523 (1988).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kbler, A. et al. A brain-computer interface controlled auditory event-related potential (p300) spelling system for locked-in patients. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1157, 90100 (2009).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Halder, S. et al. An auditory oddball brain-computer interface for binary choices. Clin. Neurophysiol. 121, 516523 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Pires, G., Nunes, U. & Castelo-Branco, M. Statistical spatial filtering for a P300-based BCI: Tests in able-bodied, and patients with cerebral palsy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurosci. Methods 195, 270281 (2011).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Sellers, E. W. & Donchin, E. A P300-based brain-computer interface: Initial tests by ALS patients. Clin. Neurophysiol. 117, 538548 (2006).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Sellers, E. W., Vaughan, T. M. & Wolpaw, J. R. A brain-computer interface for long-term independent home use. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 11, 449455 (2010).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lesenfants, D. et al. An independent SSVEP-based brain-computer interface in locked-in syndrome. J. Neural Eng. Neural Eng. 11, 035002 (2014).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Zhu, D., Bieger, J., Molina, G. G. & Aarts, R. M. A survey of stimulation methods used in SSVEP-based BCIs. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2010/702357 (2010).
Chavarriaga, R. & Milln, J. del R. Learning from EEG error-related potentials in noninvasive brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 18, 381388 (2010).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Logothetis, N. K., Pauls, J., Augath, M., Trinath, T. & Oeltermann, A. Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal. Nature 412, 150157 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N., Ruiz, S. & Sitaram, R. Learned regulation of brain metabolism. Trends Cogn. Sci. 17, 295302 (2013). An extensive review of basic and clinical neurofeedback studies using learning of metabolic brain resonses (BOLD or oxygenation) and the effects on behaviour and cognition.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
DeCharms, R. C. et al. Learned regulation of spatially localized brain activation using real-time fMRI. Neuroimage 21, 436443 (2004).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Rota, G., Handjaras, G., Sitaram, R., Birbaumer, N. & Dogil, G. Reorganization of functional and effective connectivity during real-time fMRI-BCI modulation of prosody processing. Brain Lang. 117, 123132 (2011).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Weiskopf, N. et al. Physiological self-regulation of regional brain activity using real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI): methodology and exemplary data. Neuroimage 19, 577586 (2003).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Yoo, S. S. et al. Brain computer interface using fMRI: spatial navigation by thoughts. Neuroreport 15, 15911595 (2004).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N. et al. Deficient fear conditioning in psychopathy: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 62, 799805 (2005).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Linden, D. E. J. et al. Real-time self-regulation of emotion networks in patients with depression. PLoS One http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038115 (2012).
Li, X. et al. Volitional reduction of anterior cingulate cortex activity produces decreased cue craving in smoking cessation: A preliminary real-time fMRI study. Addict. Biol. 18, 739748 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chaudhary, U., Hall, M., DeCerce, J., Rey, G. & Godavarty, A. Frontal activation and connectivity using near-infrared spectroscopy: verbal fluency language study. Brain Res. Bull. 84, 197205 (2011).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chaudhary, U. et al. Motor response investigation in individuals with cerebral palsy using near infrared spectroscopy: pilot study. Appl. Opt. 53, 503510 (2014).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Obrig, H. NIRS in clinical neurology - a 'promising' tool? Neuroimage 85, 535546 (2014).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gallegos-Ayala, G. et al. Brain communication in a completely locked-in patient using bedside near-infrared spectroscopy. Neurology 82, 19301932 (2014). The first report of a controlled case study with BCI in a completely paralyzed, locked-in patient restoring communication.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Naito, M. et al. A communication means for totally locked-in ALS patients based on changes in cerebral blood volume measured with near-infrared light. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. E90D, 10281037 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N. et al. A spelling device for the paralysed. Nature 398, 297298 (1999).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ramos-Murguialday, A. et al. Brain-machine interface in chronic stroke rehabilitation: a controlled study. Ann. Neurol. 74, 100108 (2014).
Article Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N., Murguialday, A. R. & Cohen, L. Brain-computer interface in paralysis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 21, 634638 (2008).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chou, S. M. & Norris, F. H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Lower motor neuron disease spreading to upper motor neurons. Muscle Nerve 16, 864869 (1993).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bauer, G., Gerstenbrand, F. & Rumpl, E. Varieties of the Locked-in Syndrome. J. Neurol. 221, 7791 (1979).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Beukelman, D., Fager, S. & Nordness, A. Communication support for people with ALS. Neurol. Res. Int. 2011, 714693 (2011).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Beukelman, D. & Mirenda, P. Augmentative & alternative communication: Supporting children & adults with complex communication needs. (Paul, H. Brookes, Baltimore, MD, 2005).
Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N. & Cohen, L. G. Brain-computer interfaces: communication and restoration of movement in paralysis. J. Physiol. 579, 621636 (2007).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kennedy, P. R. & Bakay, R. A. Restoration of neural output from a paralyzed patient by a direct brain connection. Neuroreport 9, 17071711 (1998).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kennedy, P. R., Bakay, R. A., Moore, M. M., Adams, K. & Goldwaithe, J. Direct control of a computer from the human central nervous system. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 8, 198202 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kennedy, P. et al. Using human extra-cortical local field potentials to control a switch. J. Neural Eng. 1, 7277 (2004).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Wilhelm, B., Jordan, M. & Birbaumer, N. Communication in locked-in syndrome: effects of imagery on salivary pH. Neurology 67, 534535 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Murguialday, A. R. et al. Transition from the locked in to the completely locked-in state: a physiological analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 122, 925933 (2011).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N. Breaking the silence: brain-computer interfaces (BCI) for communication and motor control. Psychophysiology 43, 517532 (2006).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kbler, A. & Birbaumer, N. Brain-computer interfaces and communication in paralysis: extinction of goal directed thinking in completely paralysed patients? Clin. Neurophysiol. 119, 26582666 (2008).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wolpaw, J. R. & McFarland, D. J. Control of a two-dimensional movement signal by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 1784917854 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bai, O., Lin, P., Huang, D., Fei, D. Y. & Floeter, M. K. Towards a user-friendly brain-computer interface: initial tests in ALS and PLS patients. Clin. Neurophysiol. 121, 12931303 (2010).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Thorns, J. et al. Movement initiation and inhibition are impaired in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp. Neurol. 224, 389394 (2010).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N., Piccione, F., Silvoni, S. & Wildgruber, M. Ideomotor silence: the case of complete paralysis and brain-computer interfaces (BCI). Psychol. Res. 76, 183191 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hinterberger, T. et al. Neuronal mechanisms underlying control of a brain computer interface. Eur. J. Neurosci. 21, 31693181 (2005).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hinterberger, T. et al. Voluntary brain regulation and communication with electrocorticogram signals. Epilepsy Behav. 13, 300306 (2008).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Koralek, A. C. et al. Corticostriatal plasticity is necessary for learning intentional neuroprosthetic skills. Nature 483, 331335 (2012).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Dworkin, B. R. & Miller, N. E. Failure to replicate visceral learning in the acute curarized rat preparation. Behav. Neurosci. 100, 299314 (1986). This paper describes the failure to establish instrumental learning of physiological responses in the curarized rat and possible reasons for this problem.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Stocco, A., Lebiere, C. & Anderson, J. R. Conditional routing of information to the cortex: a model of the basal ganglia's role in cognitive coordination. Psychol. Rev. 117, 541574 (2010).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Birbaumer, N. & Chaudhary, U. Learning from brain control: clinical application of braincomputer interfaces. e-Neuroforum 6, 8795 (2015).
Article Google Scholar
Furdea, A. et al. A new (semantic) reflexive brain-computer interface: in search for a suitable classifier. J. Neurosci. Methods 203, 233240 (2012).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ruf, C. A., De Massari, D., Wagner-Podmaniczky, F., Matuz, T. & Birbaumer, N. Semantic conditioning of salivary pH for communication. Artif. Intell. Med. 59, 18 (2013).
Article Google Scholar
De Massari, D. et al. Brain communication in the locked-in state. Brain 136, 19892000 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lul, D. et al. Brain responses to emotional stimuli in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J. Neurol. 254, 519527 (2007).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lul, D. et al. Life can be worth living in locked-in syndrome. Prog. Brain Res. 177, 339351 (2009).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lul, D. et al. Quality of life in fatal disease: the flawed judgement of the social environment. J. Neurol. 260, 28362843 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chaudhary, U. & Birbaumer, N. Communication in locked-in state after brainstem stroke: a brain- computer-interface approach. Ann. Transl. Med. 3, 24 (2015).
Google Scholar
Simeral, J. D., Kim, S. P., Black, M. J., Donoghue, J. P. & Hochberg, L. R. Neural control of cursor trajectory and click by a human with tetraplegia 1000 days after implant of an intracortical microelectrode array. J. Neural Eng. 8, 025027 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kbler, A. et al. Self-regulation of slow cortical potentials in completely paralyzed human patients. Neurosci. Lett. 252, 171174 (1998).
Article Google Scholar
Piccione, F. et al. P300-based brain computer interface: reliability and performance in healthy and paralysed participants. Clin. Neurophysiol. 117, 531537 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sellers, E. W., Ryan, D. B. & Hauser, C. K. Noninvasive brain-computer interface enables communication after brainstem stroke. Sci. Transl. Med. 6, 257re7 (2014).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cirstea, M. C., Ptito, A. & Levin, M. F. Arm reaching improvements with short-term practice depend on the severity of the motor deficit in stroke. Exp. Brain Res. 152, 476488 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Young, J. & Forster, A. Review of stroke rehabilitation. BMJ 334, 8690 (2007).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Saka, O., McGuire, A. & Wolfe, C. Cost of stroke in the United Kingdom. Age Ageing 38, 2732 (2008).
Article Google Scholar
Langhorne, P., Bernhardt, J. & Kwakkel, G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet 377, 16931702 (2015).
Article Google Scholar
Hendricks, H. T., van Limbeek, J., Geurts, A. C. & Zwarts, M. J. Motor recovery after stroke: a systematic review of the literature. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 83, 16291637 (2002).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ward, N. S. & Cohen, L. G. Mechanisms underlying recovery of motor function after stroke. Arch. Neurol. 61, 18441848 (2004).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Taub, E., Uswatte, G. & Pidikiti, R. Constraint-induced movement therapy: a new family of techniques with broad application to physical rehabilitation a clinical review. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 36, 237251 (1999).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wolf, S. L. et al. Effect of constraint-induced movement therapy on upper extremity function 3 to 9 months after stroke: the EXCITE randomized clinical trial. JAMA 296, 20952104 (2006).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Buch, E. R. et al. Parietofrontal integrity determines neural modulation associated with grasping imagery after stroke. Brain 135, 596614 (2012).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Belda-Lois, J.-M. et al. Rehabilitation of gait after stroke: a review towards a top-down approach. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 8, 66 (2011).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Chollet, F. et al. Fluoxetine for motor recovery after acute ischaemic stroke (FLAME): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 10, 123130 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Savitz, S. I. et al. Stem cells as an emerging paradigm in stroke 3: enhancing the development of clinical trials. Stroke 45, 634639 (2014).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ganguly, K., Dimitrov, D. F., Wallis, J. D. & Carmena, J. M. Reversible large-scale modification of cortical networks during neuroprosthetic control. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 662667 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gulati, T. et al. Robust neuroprosthetic control from the stroke perilesional cortex. J. Neurosci. 35, 86538661 (2015).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Nishimura, Y., Perlmutter, S. I., Eaton, R. W. & Fetz, E. E. Spike-timing-dependent plasticity in primate corticospinal connections induced during free behavior. Neuron 80, 13011309 (2013). This paper describes the neurophysiological bases of BCI applications in spinal cord injury.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lucas, T. H. & Fetz, E. E. Myo-cortical crossed feedback reorganizes primate motor cortex output. J. Neurosci. 33, 52615274 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ang, K. K. et al. Brain-computer interface-based robotic end effector system for wrist and hand rehabilitation: results of a three-armed randomized controlled trial for chronic stroke. Front. Neuroeng. http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fneng.2014.00030 (2014).
Ono, T. et al. Brain-computer interface with somatosensory feedback improves functional recovery from severe hemiplegia due to chronic stroke. Front. Neuroeng. http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fneng.2014.00019 (2014).
Pichiorri, F. et al. Braincomputer interface boosts motor imagery practice during stroke recovery. Ann. Neurol. 77, 851865 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kasahara, K., DaSalla, C. S., Honda, M. & Hanakawa, T. Neuroanatomical correlates of braincomputer interface performance. Neuroimage 110, 95100 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bensmaia, S. J. & Miller, L. E. Restoring sensorimotor function through intracortical interfaces: progress and looming challenges. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 313325 (2014).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ren, X. et al. Enhanced low-latency detection of motor intention from EEG for closed-loop brain-computer interface applications. Biomed. Eng. IEEE Trans. 61, 288296 (2014).
Article Google Scholar
Jiang, N., Gizzi, L., Mrachacz-Kersting, N., Dremstrup, K. & Farina, D. A braincomputer interface for single-trial detection of gait initiation from movement related cortical potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol. 126, 154159 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Collinger, J. L. et al. High-performance neuroprosthetic control by an individual with tetraplegia. Lancet 381, 557564 (2013).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ouzk, M. Towards concerted efforts for treating and curing spinal cord injury (Council of Europe Parliamentary Assembly document 9401). https://assembly.coe.int/nw/xml/XRef/X2H-Xref-ViewHTML.asp?FileID=9680&lang=en (2002)
Van Den Berg, M. E., Castellote, J. M., Mahillo-Fernandez, I. & De Pedro-Cuesta, J. Incidence of spinal cord injury worldwide: a systematic review. Neuroepidemiology 34, 184192 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wolpaw, J. R. The complex structure of a simple memory. Trends Neurosci. 20, 588594 (1997).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wang, W. et al. An electrocorticographic brain interface in an individual with tetraplegia. PLoS ONE http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055344 (2013).
Pfurtscheller, G., Mller, G. R., Pfurtscheller, J. & Gerner, H. J. & Rupp, R. 'Thought' - Control of functional electrical stimulation to restore hand grasp in a patient with tetraplegia. Neurosci. Lett. 351, 3336 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Nguyen, J. S., Su, S. W. & Nguyen, H. T. Experimental study on a smart wheelchair system using a combination of stereoscopic and spherical vision. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 45974600 (2013).
PubMed Google Scholar
Kasashima-Shindo, Y. et al. Braincomputer interface training combined with transcranial direct current stimulation in patients with chronic severe hemiparesis: proof of concept study. J. Rehabil. Med. 47, 318324 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Enzinger, C. et al. Brain motor system function in a patient with complete spinal cord injury following extensive brain-computer interface training. Exp. Brain Res. 190, 215223 (2008).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
King, C. E. et al. The feasibility of a brain-computer interface functional electrical stimulation system for the restoration of overground walking after paraplegia. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 12, 80 (2015).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pfurtscheller, G., Guger, C., Mller, G., Krausz, G. & Neuper, C. Brain oscillations control hand orthosis in a tetraplegic. Neurosci. Lett. 292, 211214 (2000). The first paper demonstrating noninvasive brain control using a sensorimotor rhythm braincomputer interface in a high spinal cord patient.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Courtine, G. & Bloch, J. Defining Ecological Strategies in Neuroprosthetics. Neuron 86, 2933 (2015).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
van den Brand, R. et al. Restoring voluntary control of locomotion after paralyzing spinal cord injury. Science 336, 11821185 (2012).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Combaz, A. et al. A comparison of two spelling brain-computer interfaces based on visual P3 and SSVEP in locked-in syndrome. PLoS ONE http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073691 (2013).
Bardin, J. C. et al. Dissociations between behavioural and functional magnetic resonance imaging-based evaluations of cognitive function after brain injury. Brain 134, 769782 (2011).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Monti, M. M. et al. Willful modulation of brain activity in disorders of consciousness. N. Engl. J. Med. 362, 579589 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Schnakers, C. et al. Detecting consciousness in a total locked-in syndrome: an active event-related paradigm. Neurocase 15, 271277 (2009).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lul, D. et al. Probing command following in patients with disorders of consciousness using a brain-computer interface. Clin. Neurophysiol. 124, 101106 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar